Integrated Document No. 17/VBHN-BGDDT dated May 15, 2014 of the Ministry of Education and Training integrates the Decisions on promulgation of regulation on formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system
ATTRIBUTE
| Issuing body: | Ministry of Education and Training | Effective date: | Updating |
| Official number: | 17/VBHN-BGDDT | Signer: | Bui Van Ga |
| Type: | Consolidated Text | Expiry date: | Updating |
| Issuing date: | 15/05/2014 | Effect status: |
Known
Please log in to a subscriber account to use this function. Don’t have an account? Register here |
| Fields: | Education - Training - Vocational training |
THE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING
Integrated Document No.17/VBHN-BGDDT dated May 15, 2014 of the Ministry of Education and Training integrates the Decisions onpromulgation of regulation on formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system
Decision No. 43/2007/QD-BGDDT dated August 15, 2007 by the Minister of Education and Training on promulgation of Regulation on formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system that took effect on August 31st, 2007 is amended and supplemented by:
Circular No. 57/2012/TT-BGDDT dated December 27th, 2012 by the Minister of Education and Training amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Regulation on formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system, enclosed with Decision No. 43/2007/QD-BGDDT dated August 15th, 2007 by the Minister of Education and Training that took effect on February 10th, 2013.
Pursuant to the Law on Education dated June 14, 2005;
Pursuant to Decree No. 86/2002/ND-CP dated November 05, 2002 by the Government defining the functions, tasks, entitlements and organizational structure of Ministries and ministerial-level agencies;
Pursuant to the Decree No. 85/2003/ND-CP dated July 18th2003 by the Government defining the functions, tasks, entitlements and organizational structure of the Ministry of Education and Training;
At the request of Director of Undergraduate Education and Higher Education Department,
Article 1.To attach with this Decision the Regulation on formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system.
Article 2.This Decision takes after 15 days counting from the day it is posted on Official gazette.This Decision replaces the Decision No. 31/2001/QD-BGD&DT dated July 30, 2001 by the Minister of Education and Training on pilot project of training, testing and graduation recognition for formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system.
Article 3.The Chief of the Ministry Office, Director of Higher Education Department, Heads of relevant units that are affiliated to the Ministry of Education and Training, Director of universities and institutes; Directors of universities and colleges are responsible for implementing this Decisions./.
Certification of the Integrated Document
For the Minister
The Deputy Minister
Bui Van Ga
REGULATION
ON FORMAL UNDERGRADUATE EDUCATION APPLYING ACADEMIC CREDIT SYSTEM
Chapter I
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1. Scope of adjustment and subject of application
1. This Regulation provides for formal undergraduate education applying academic credit system, including: training, testing; consideration and recognition of graduation.
2. This Regulation applies to students of formal courses of university level and college level in institutes, universities and colleges (hereinafter referred to as schools) that apply the course credit system.
Article 2. Training programs and syllabuses
1. A curriculum must specify: training level; training subject, enrolment requirements and graduation requirements; training targets and knowledge and skill standards when students graduate; theory, practice and internship load; training plan according to designed schedule; methods and forms of training; forms of evaluation of studying results; conditions for following the curriculum.
2. Each curriculum shall be used for a discipline (single-disciplinary education) or a number of disciplines (multidisciplinary education; disciplinary and sub-disciplinary education; concurrent-curricula education) and shall be structured from courses of fundamental subjects and professional subjects.
3. Outline of each course must specify the number of credits, preconditions (if any), theory and practice contents, methods of evaluation of course results, studying books, reference documents and conditions of experiment, practice and internship serving the course.
4. Directors of schools shall promulgate the curricula to be applied in their schools provided that the academic load of each curriculum must not less than 180 credits, applicable to 6-year university’s programs; 150 credits, applicable to 5-year university’s programs; 120 credits, applicable to 4-year university’s programs; 90 credits, applicable to 3-year college s programs or 60 credits, applicable to 2-year college’s programs.
Article 3. Courses and credits
1. A “course” means a nearly complete amount of knowledge that student can accumulate during the study process. Most courses carry 2 to 4 credits, training contents are provided completely and evenly during a semester. Knowledge in each course shall be corresponding to a level according to the course design and shall be structured as a part of a subject or a collection of subjects. Each course shall be designate with a particular code regulated by a particular school.
2. Courses are divided into compulsory courses and elective courses.
a) A compulsory course is the course containing the main knowledge contents of a curriculum that a student must accumulate;
b) An elective course contains the necessary knowledge that students are allowed to select themselves according to the guidance of their schools to diversify the specialties or select freely to accumulate sufficiently courses as required.
3. Credits are used for calculating the academic load of students. A credit shall be equivalent to 15 theory periods; 30 - 45 periods of practice, experiment or discussion; 45 - 90 hours of internship; 45 - 60 hours of thesis, coursework or graduate thesis.
Regarding theory courses or practical courses, students shall spend at least 30 self-preparation hours to acquire a credit.
Directors of undergraduate schools shall provide specific regulations on the number of periods/hours for specific courses according to the characteristics of their schools.
4.Directors of undergraduate schools shall provide regulations on the calculation of teaching duration of lecturers for specific courses, including amount of on-class time and practice/internship time, amount of time for preparing self-study load for students and evaluating students’ self-study results and amount of time lecturers meet their students outside the classes.
5. A study period shall last 50 minutes.
Article 4. Time of education
Time of education of a school is from 8 a.m to 8 p.m every day. Depending on the actually conditions of schools, Directors shall provide specific regulations on time of education of their schools.
Depending on the number of students, number of classes and facilities of schools, heads of registrar offices shall arrange the timetable for specific classes.
Article 5. Evaluation of study results
Study result of a student shall be evaluated after every semester according to the following criteria:
1. The number of courses that the student registered at beginning of every semester (hereinafter to as the registered academic load).
2. The semester GPA which is the weighted average of grade points of courses that the student registered in such semester, where weighing factor is the number of credits of the respective courses.
3. Amount of accumulated knowledge which is calculated by the total of credits of courses that are graded in A - D range from the beginning of the program.
4. Cumulative GPA which means the average of grade points of the course graded in A - D range that the student has accumulated from the beginning of the program to the time of evaluation at the end of a semester.
Chapter II
EDUCATION ORGANIZATION
Article 6. Education time and schedule
1. School managers shall provide education in academic programs, academic years and academic semesters.
a) A program is a duration that is designed for students to complete a specific curriculum. Depending on the curriculum, the program shall be specified as follows:
- College education programs shall last 2 - 3 years depending on the specialties, applicable to students with high school diplomas or vocational degrees or 1.5 - 2 years, applicable to students with vocational degrees in the same specialties;
- University education programs shall last 4 - 6 years depending on the specialties, applicable to students with high school diplomas or vocational degrees or 2.5 - 4 years, applicable to students with vocational degrees in the same specialties or 1.5 -2 years, applicable to students with college s degrees in the same specialties.
b) An academic year contains 2 main semesters with at least 15 actual-study weeks and 3 test weeks. Besides 2 main semesters, the Director shall consider providing an auxiliary semester for repeat of courses, make-up study or accelerated study. An auxiliary semester shall contain at least 5 actual-study weeks and 1 test weeks.
2. Depending on the required amount and contents of knowledge specified for a curriculum, the Director shall apportion the courses to specific school years/semesters.
3. Time limit for completion of a curriculum shall include the designed duration of the curriculum specified in clause 1 of this Article plus 2 semesters (applicable to programs lasting under 3 years) or 4 semesters (applicable to programs lasting 3 - 5 years) or 6 semesters (applicable to programs lasting 5 - 6 years).
Depending on the training conditions of the school, the Director shall regulate the time limit for specific curriculum but not exceeding twice the designed duration of such curriculum.
Entities eligible for priority policies according to the provisions of the Regulation on enrolment for formal undergraduate education shall not be required to comply with the regulations on time limit for completion of the curriculum.
Article 7. Enrolment application
1.When carrying out the enrolment application, students must submit all papers as provided for by applicable Regulation on enrolment for formal undergraduate education. All such papers of different students must be contained in different packages and must be retained and managed as regulated by the Directors of schools.
2. After checking the applications, if the documents are satisfactory, registrar offices shall request the Directors to sign the decisions on recognition of the applicant as the official students of the school and grant them:
a) Student ID card;
b) Studying registration book;
c) Advisor’s information slip.
3. Any enrolment application procedures shall be completed within the time limit prescribed in the applicable Regulations on enrolment for formal undergraduate education.
4. Students who have enrolled in the program shall be provided with sufficient information about objectives, contents and the curriculum sequence, training regulation, obligations and rights of students.
Article 8. Arrangement of student to curricula or discipline
1. Regarding schools determining the admission score according to the curricula (or the disciplines) in enrolment examination, school managers shall arrange candidates satisfying the enrolment requirements to enroll in the curricula (or disciplines) they have applied for.
2. Regarding schools determining the admission scores according to the groups of curricula (or the groups of disciplines) in enrolment examination, school managers shall publish at the beginning of the program the admission target of specific curricula (or disciplines). Depending on students’ choice about curricular (or disciplines), their examination scores and study results, they shall be arranged to appropriate curricula (disciplines). Each student may apply for some curricula (or disciplines) in order of priority. Directors of schools shall be responsible for regulating the quantity and criteria for specific curricula (or disciplines) for students to register.
Article 9. Class organization
Classes shall be organized by courses depending on the registration of students in specific semesters. Directors of schools shall be responsible for regulating the minimum number of students of specific classes in specific courses. If the number of students registering for a class is lower than the minimum number, the class shall be cancelled and students shall register to transfer to another class. Students shall ensure to register at least equal to the minimum academic load for a semester.
Article 10. Courses registration
1. At the beginning of a year, the school shall make announcement about the planned schedule for specific curricula in each semester, lists of planned compulsory and elective courses, syllabus and preconditions for registering for the courses, schedule and forms of tests applied to the courses.
2. Before the beginning of a semester, depending on study capacity and condition of themselves, students shall register with the registrar office for the courses in the semester. The courses can be registered in 3 forms: early registration, normal registration and late registration.
a) Early registration is the form in which the registration is carried out 2 months before the semester starts;
b) Normal registration is the form in which the registration is carried out 2 weeks before the semester starts;
c) Late registration is the form in which the registration is carried out within 2 first weeks of the main semester or in the first week of the auxiliary semester, enabling the students to register more courses or transfer the courses in case the class is cancel.
Depending on the training conditions of schools, Directors shall consider and decide a suitable form of registration.
3. The minimum number of credits a student shall register per semester is specified as follows:
a) 14 credits per semester, except for the last semester of a program, applicable to normal students;
b) 10 credits per semester, except for the last semester, applicable to poor-ranking students;
c) The number of credits a student registers in the auxiliary semesters is not limited.
4. Poor-ranking students are allowed to register not exceeding 14 credits per semester.Normal-ranking students are not limited on the number of credits.
5. The registration of courses shall ensure the preconditions of each course and the order of specific curriculum.
6. The registrar office shall accept a course registration only when the student has his/her study registration book approved by his/her advisor or according to the regulation of the Director. The credits students registered per semester shall be recorded to the course registration papers and shall be retained by the registrar office.
Article 11. Course withdrawals
1. The withdrawal of courses of the registered academic load shall be performed after 2 weeks since the beginning of main semesters or after 1 week since auxiliary semester. Depending conditions of their schools, Directors shall regulate time limit for withdrawing courses of the registered academic load. Upon the expiry of such time limit, courses shall be retained in course registration papers and students shall receive an F grade if they do not attend the class without permission.
2. Conditions for course withdrawals:
a) Students shall submit applications to the registrar office;
b) The withdrawals shall be approved by the advisors or according to the regulation of the Directors;
c) Students shall not commit any violations against the provisions of clause 3 Article 10 of this Regulation.
A student shall absent only from the class of the course he/she has withdrawn when the responsible lecturer has received the notification of the registrar office.
Article 12. Repeat of courses
1. Any student that has a compulsory course receiving F grade shall repeat the course in any of the following semesters until they get A, B, C or D grade for such course.
2. Any student that has an elective course receiving F grade shall apply for repeat of the course or register a similar course.
3. Apart from the cases specified in clauses 1 and 2 of this Article, students may retake or replace the course that receive D grade for cumulative GPA forgiveness.
Article 13. Sick leave
Any students wishing to be on sick leave in a course or in an exam stage shall file an application to the dean of the management faculty of the course within 1 week since he/she got sick, enclosed with the written verification of medical division of the school or a medical agency in local area or a hospital.
Article 14. Ranking of academic years and student’s status
1. After each semester, depending on the number of accumulated credits, students shall be classified into: freshman, sophomore, junior, senior, 5thyear senior, 6thyear senior. Depending on academic load of specific curricula specified in clause 4 Article 2 of this Regulation, Directors shall specify limit of academic load where ranks of academic years shall be changed.
2. After each semester, depending on the cumulative GPA, students shall be classified as follows:
a) Normal grade: if the cumulative GPA is 2.00 or higher.
b) Poor grade: if the cumulative GPA is under 2.00 but does not fall in cases subject to expulsion.
3. The result of the auxiliary semester shall be included in the result of the main semester that is immediately before the auxiliary semester for study ranking.
Article 15. Temporary absence from schools
1. A student may file an application for temporary absence from school and reserve of the results in the following cases:
a) The student joins the armed forces;
b) The student is sick or has an accident that needs to receive long-term treatment; such case shall be verified by the medical agency;
c) Due to personal reasons. In this case, the student shall have completed at least 1 semester and must not fall in the cases subject to academic expulsion provided for in Article 16 of this Regulation and his/her cumulative GPA shall not be under 2.00. Duration of the temporary absence from school due to personal reasons shall be included in the study duration specified in clause 3 Article 6 of this Regulation.
2. After the temporary absence, the student wishing to continue pursuing his/her degree shall submit an application to the Director not later than 1 week before the new semester starts.
Article 16. Warning about study results, expulsion
1. The warning about study results shall be conducted according to different semesters to remind students who have poor study results to formulate suitable study plans so as to graduate within the time limit applicable to the curricula. The warning about students’ study results shall be conducted in the following cases:
a) The cumulative GPA is under 1.20, applicable to the freshmen; under 1.40, applicable to the sophomores; under 1.60, applicable to the junior or under 1.80, applicable to the others;
b) The semester GPA is under 0.80, applicable to the first semester, or under 1.00 applicable to the next semesters;
c) Total of credits of courses graded F that have not been forgiven, counting from the beginning of the curricula to the time of evaluation, exceeds 24.
Depending of characteristics of schools, their Directors shall regulate to issue warning in one or two of the three cases above and shall prescribe the number of warnings about study results that must not exceed 2 consecutive times.
2. After a semester, a student shall incur expulsion in any of the following cases:
a) The number of warnings about study results exceeds the limit prescribed by the Directors;
b) The student has been studying at school for longer than the time limit specified in clause 3 Article 6 of this Regulation;
c) The student incurs disciplinary penalties for the impersonation at the examination for the second time according to regulations in clause 2 Article 29 of this Regulation or is subject to being crossed out of the list of students of the school.
3. Not later than 1 month since the decision on expulsion is issued, the school shall send a notification to the local government of the place at which the student has permanent resident status. If there is a similar education curriculum of lower level at the school where the student is studying or at another school, the student subject to academic expulsion specified in points a, b and c clause 2 of this Article may apply for transfer to such curriculum; a part of results of the completed courses shall be reserved. The Director shall consider deciding the reserve of study results in specific cases.
Article 17. Concurrent curricula
1. Concurrent curricula are for students satisfying conditions specified in clause 2 of this Article who wish to follow a second curriculum to gain 2 degrees when they graduate.
2. Requirements for following concurrent curricula:
a) The specialties of the second curricula shall be different from the one of the first curricula;
b) Students have finished the first semester of the first year of the first curricula and the students do not fall in cases subject to poor-ranking;
c) During the time when students follow concurrent curricula, if their semester GPA fall under 2.00, they must suspend the second curricula since the immediately next semesters.
3. The time limit for a student following concurrent curricula to complete his/her study is the time limit provided for the first curriculum specified in clause 3 Article 6 of this Regulation. When following the second curricula, students will have their results of the courses having similar academic load of the first curricula reserved.
4. A student shall be eligible for consideration for graduation in the second curriculum only when he/she is eligible for graduation in the first curriculum.
Article 18. School transfer
1. A student may be considered for school transfer in the following conditions:
a) His/her family changes resident place when he/she is still in study process or the student faces disadvantage situations that he/she must transfer to a school near to his/her residence to facilitate his/her study;
b) The student transfers to a school providing the same major or speciality with the one he/she is participating;
c) The transfer is approved by both the Director of the current school and the new school (or target school);
d) The student is not of the cases forbidden from school transfer specified in clause 2 of this Article.
2. School transfer shall be forbidden in the following cases:
a) The student has taken the enrollment exam like other people but did not pass or have the result lower than the benchmark of the target school;
b) The student is other than those eligible for enrolling to the target school;
c) The student is a freshman or a senior;
d) The student is incurring a disciplinary measure of warning or higher.
3. Procedures for school transfer:
a) Any student wishing to transfer school shall submit an application according to the regulation of the school;
b) The Director of the target school may decide to accept or not; decide the future study of the student, the recognition of the courses of the student that are reserved and the amount of courses that the student needs to supplement on the basis of the difference between the curricula of the schools before and after the transfer.
Chapter III
TEST
Article 19. Course evaluation
1. Regarding the courses containing only theory contents or both theory and practice contents: Depending on the characteristics of the course, the course s grade shall be calculated on the basis of a number of or all of the on-going scores, including the scores of the regular tests during the course; the scores of awareness and class participation of student; the scores of the practice activities; the score of attendance; the mid-term test result; the score of thesis and the final test results, where the final test results shall be always compulsory and have the weighing factor of not under 50%.
The choice of on-going evaluation and weighing factors of the scores as well as the formula for calculating the final result for evaluation shall be designed by the lecturers and approved by the Directors of schools and shall be specified in syllabuses of the courses.
2. Regarding practice courses: students shall attend sufficiently the practice lessons. The average scores of the practice lessons of a course in a semester that are rounded to 1 decimal place shall be the final results of such practice course.
3. The lecturer in charge of the course shall be responsible for designing the test questions and giving on-going evaluation, excluding the final tests.
Article 20. Final tests
1. At the end of each semester, final tests shall be organized, including 1 stage only or 1 main stage and 1 auxiliary stage. The auxiliary stage shall be organized for students who fail to participate in the main stage or received an F grade at the main stage and shall be organized not earlier than 2 weeks after the main stage.
2. Time for review for the test of a course shall be proportional to the number of credits of such course that is at least 2/3 days for each credit. Directors of schools shall specify the time for review for the tests and the dates of test.
Article 21. Design of question sheets, form of tests, marking and the limit number for taking final tests
1. The final test questions shall be appropriate to the contents of the course specified in the curriculum. Questions in question sheets may be designed or taken from the question bank according to the instruction of the Directors of schools.
2. The forms of final tests could be multiple-choice test, writing test, oral test, thesis, coursework or the combination of these forms. Directors of schools shall be responsible for approving the suitable form for each course.
3. The marking of final test containing theory questions only and the marking of theses and coursework shall be conducted by 2 lecturers.
Directors of schools shall provide regulations on the retention of test papers during and after marking. Test papers, theses and coursework shall be retained for at least 2 years from the day of test or the day on which the theses/coursework is submitted.
4. The marking of final tests in form of oral test shall be carried out by 2 lecturers. The scores of oral tests shall be published when the test finishes. If the two lecturers who are in charge of marking the test fail to conclude agreement about a score, it shall be decided by the head of subject groups of the dean of the faculty.
The final test scores and the average scores of a course shall be written on 3 copies of score sheet according to the form regulated by the school management boards and shall be signed by the marking lecturers. One of which shall be retained at the subject group management, another shall be sent to the faculty management and the other shall be sent to the registrar office within 1 week since the marking finishes.
5. Any student who is absent from the final test without good and sufficient reason shall be considered having taken the test once and received 0 point for the main stage. Such student may take the auxiliary stage right then (if any) if allowed by the dean of the faculty.
6. Any student who is absent from the main stage of final test with good and sufficient reasons may take the auxiliary stage right then (if any) if allowed by the dean of faculty, the result in this case shall be considered the first-time score. If there is not any auxiliary stage or the student fails the auxiliary stage, such student shall take the ones of the next semesters or of auxiliary semesters.
Article 22. On-going evaluation and course grades
1. On-going and final-exam scores shall be graded according to 10-mark scale and rounded to 1 decimal place.
2. Course grades shall be determined by the total scores of all the on-going evaluations of courses multiplying the respective weighing factor. Course grades shall be rounded to 1 decimal place then converted into letter as follows:
a) Pass:
A (8.5 - 10) Excellent
B (7.0 - 8.4) Good
C (5.5 – 6.9) Satisfactory
D (4.0 – 5.4) Poor
b) Not pass: F (under 4.0) F
c) Regarding courses without elements for calculating GPA, the following grades shall be used:
I Incomplete
X No grade reported.
d) Regarding courses in which scores are permissible to transferred, the grading “R" shall be written besides the results.
3. The grading A, B, C, D, F shall be applied in the following cases:
a) Courses where students gain sufficient on-going scores, including cases where students absence from class or exams without permission subject to receiving 0 point;
b) Such grades are transferred from “I” grades when on-going scores on which the students were permitted to fall behind have been given.
c) Such grades are transferred from “X” grades.
4. Apart from the cases specified in clause 3 of this Article, “F” grades shall be assigned to students who commit violations against the regulations on examination and are subject to receiving F grades according to decisions.
5. “I” grades shall be applied in the following cases:
a) During the courses or during the final tests, students get sick or have accidents that they cannot take the exams; such cases shall be approved by the deans of the management faculties;
b) Students cannot take the on-going tests or exams due to objective reasons and are approved by the deans of faculties.
Except for the special cases regulated by the Directors, before new semesters start, students receiving “I” grades shall complete the incomplete tests to be eligible for transfer of scores. If students have not completed the courses and scores have not been transferred but such students are not subject to expulsion, they shall be allowed to continue their study in the next semesters.
6. “X” grades shall be applied in the courses of which the results of students have not been sent to the registrar offices.
7. “R” grades shall be applied in the following cases:
a) The course results that are graded A, B, C or D in the assessment at the beginning of the semester (if any) for a number of courses of which exams are organized early enabling the accelerated study.
b) The courses whose results are recognized, applicable to students who are transferred from other schools or other curricula.
Article 23. Calculation of GPA
1. Before calculating semester GPA and the cumulative GPA, the grades in words of each course shall be converted into numbers (4-mark scale) as follows:
A is equivalent to 4
B is equivalent to 3
C is equivalent to 2
D is equivalent to 1
F is equivalent to 0
If the scale has more levels, the Director shall regulate the conversion of such in-word grades into corresponding number grades with 1 decimal place.
2. The semester GPA and the cumulative GPA shall be calculated according to the following formula and rounded to 2 decimal places:
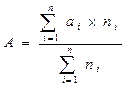
Where:
Ais the semester GPA or the cumulative GPA
aiis the grade of the ithcourse
niis the credits of the ithcourse
nis the total number of courses.
The semester GPA used for consideration for scholarships or awards after every semester shall be calculated using only the result of the first stage of test. The semester GPA and the cumulative GPA used for consideration for expulsion or grading of learning results or the graduate grading shall depend on the highest final test result of each courses.
Chapter IV
CONSIDERATION AND RECOGNITION OF GRADUATION
Article 24. Internship and graduate thesis
1. At the beginning of the last semester, student may register for doing graduate thesis or studying a number of professional courses as follows:
a) Graduate thesis: applicable to students satisfying the requirements of school. Graduate thesis means a course carrying not more than 14 credits (applicable to university level) or 4 credits (applicable to college level). Directors shall regulate the specific amount of credits in accordance with the training requirements of the schools.
b) Professional courses: any student who is not eligible for doing graduate thesis and has not accumulated sufficiently required credits shall take some more professional courses.
2. Depending on the conditions of school and peculiarities of each discipline, Directors shall provide regulations on:
a) Requirements for students to register for doing graduate thesis;
b) Form and time of doing graduate thesis;
c) Form of graduate thesis evaluation;
d) Tasks of supervisors; responsibilities of subject groups and faculty managers towards students during the formulation of graduate thesis.
3. Regarding graduate thesis of disciplines requiring a great amount of time for experiment or survey, school managers may combine the time for the graduate thesis formulation with time for internship.
Article 25. Graduate thesis evaluation
1. Depending on specific curriculum, Directors of schools shall regulate methods of evaluation of graduate thesis. The evaluation of each graduate thesis shall be conducted by 2 lecturers.
2. Theses shall be graded in words according to the regulations in points a and b clause 2 Article 22 of this Regulation. Grades of theses shall be included in the final cumulative GPA.
3. Any student having thesis receiving F grade shall redo the graduate thesis or take some more professional courses whose total number of credits is equivalent to the one of the graduate thesis.
Article 26. Internship and conditions for consideration for graduation applicable to a number of peculiar disciplines
Regarding a number of peculiar disciplines in the fields of Art, Architecture, Medicine, Sport, Directors shall provide regulations on contents and forms of internship; form of evaluation of graduate theses; conditions for consideration and recognition of graduation according to the characters of specific curriculum.
Article 27. Conditions for consideration and recognition of graduation
1.Any student shall satisfy the following conditions to be considered and recognized graduation:
a) The student is not liable to criminal prosecution or is not incurring an academic suspension until the time of consideration for graduation;
b) Required courses and academic load as prescribed in Article 2 of this Regulation have been accumulated sufficiently;
c) The final cumulative GPA is 2.00 or higher;
d) Requirements on the grades of the courses belonging to the main discipline and other requirements regulated by the Director have been satisfied;
dd) The student has been issued with the certificates of completion of Military Education courses, applicable to students of disciplines that are not specialized in military education, and has completed physical education courses, applicable to students of disciplines that are not specialized in physical education) An application for recognition of graduation has been sent to the registrar office, applicable to students eligible for graduation before or after schedule.
2. After each semester, the Graduation Consideration Council shall depend on the conditions for recognition of graduation specified in clause 1 of this Article to formulate the list of students eligible for graduation.
The Graduation Consideration Council shall include the Director or the authorized Vice Director of the School as the Chairperson, the head of registrar office as the Secretary and the deans of faculties and head of the student affair division as members.
3. Depending on the request of the Graduation Consideration Council, the Director shall sign the decision on recognition of graduation for eligible students.
Article 28. Issuance of the Certificate of graduation, reserve study and transfer of curriculum and form of education
1. The Certificates of graduation from university/college shall be issued according to the main discipline (single-disciplinary or multi-disciplinary education). The graduate grades shall be determined according to the final cumulative GPA as follows:
a) Excellent: Cumulative GPA is from 3.60 to 4.00;
b) Good: Cumulative GPA is from 3.20 to 3.59;
c) Fair good: Cumulative GPA is from 2.50 to 3.19;
d) Average: Cumulative GPA is from 2.00 to 2.49;
2. The graduate grade of a student having the final results at excellent or good level shall be 1-level degraded in the following cases:
a) The number of failed credits exceeds 5% of the total credits assigned to the curriculum;
b) The student has incurred a disciplinary measure of warning level or higher during the time he/she studies at the school.
3. The study results of students shall be recorded to the transcript and shall be sorted by courses. The transcript shall state whether the specialty is the specialties are main or auxiliary ones (if any).
4. If the study results of student satisfy the regulation in clause 1 Article 27 of this Regulation for the curricula corresponding to different disciplines, then the student shall be granted different graduate certificates corresponding to such disciplines.
5. If a student has not completed a military education or physical education course but the time limit of study has expired, within 5 years since his/her study is terminated, he/she may return to school to complete the course to be eligible for graduation.
6. Any student who does not graduate shall be granted a certificate of courses have been completed at the school. Such student may apply for transfer to another curriculum according to the regulations in clause 2 Article 16 of this Regulation.
Chapter V
ORGANIZATION OF IMPLEMENTATION
Article 29. Disciplinary penalties for students committing violations against the regulations on examination
1. During the on-going tests, the preparation of theses, coursework or mid-term tests, final tests, preparation of graduate theses, any student committing violations against the regulations shall be imposed disciplinary penalties for specific violations.
2. Any student who takes an exam by the name of another student and any student who requests another to take an exam by his/her name shall incur a 1-year academic suspension (applicable to the initial violations) or an academic expulsion (applicable to the second violations).
3. Except for the cases specified in clause 2 of this Article, violation levels and penalties imposed on students who commit violations shall comply with the provisions in the Regulation on formal undergraduate education enrollment./.
Article 29a. Organization of implementation
1. School managers shall formulate plans and route for education applying academic credit system in accordance with specific conditions of their schools.
2. On the basis of provisions of this Regulation and depending on specific conditions of schools and education route towards education fully applying academic credit system, school managers shall formulate regulations of their own schools on education applying academic credit system for formal education, working while studying, distance education and bridge-program education.
3. Periodically, school managers shall conduct inspection and assessment of the implementation, supplementation and modification of curricula and regulations applicable to education applying academic credit system, ensuring that such curricula and regulations are suitable for actual conditions and route of education applying academic credit system of schools.
4. School managers may conduct assessment and recognition of education procedures, education contents and value of credits of other schools and vice versa as the basis for recognizing accumulated knowledge of students who apply for school transfer, bridge program or further education.
5.In recruitment, final study results of students receiving education applying academic credit system and students receiving education applying yearly system shall be converted according to graduate grades (according to guidance) to be compared.
VIETNAMESE DOCUMENTS
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
ENGLISH DOCUMENTS
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here


