Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHDT Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam
ATTRIBUTE
| Issuing body: | Ministry of Planning and Investment | Effective date: |
Known
Please log in to a subscriber account to use this function. Don’t have an account? Register here |
| Official number: | 02/2025/TT-BKHDT | Signer: | Nguyen Chi Dung |
| Type: | Circular | Expiry date: | Updating |
| Issuing date: | 03/01/2025 | Effect status: |
Known
Please log in to a subscriber account to use this function. Don’t have an account? Register here |
| Fields: | Investment |
|
THE MINISTRY OF PLANNING AND INVESTMENT No. 02/2025/TT-BKHDT |
THE SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Hanoi, January 3, 2025 |
CIRCULAR
On the Set of Statistical Indicators for
Sustainable Development of Vietnam
_____________________
Pursuant to the Statistics Law dated November 23, 2015, and the Amending and Supplementing a Number of Articles of, and the Appendix on the List of National Statistical Indicators to, the Statistics Law dated November 12, 2021;
Pursuant to the Government's Decree No. 94/2016/ND-CP dated July 1, 2016, detailing and guiding the implementation of a number of articles of the Statistics Law;
Pursuant to the Government's Decree No. 94/2022/ND-CP dated November 7, 2022, prescribing the statistical indicator in the national statistical indicators system, and process of compiling gross domestic product indicators and gross product indicators in provinces and centrally run cities;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 62/2024/ND-CP dated June 7, 2024, amending and supplementing a number of articles and appendices of the Government's Decree No. 94/2016/ND-CP dated July 1, 2016, detailing and guiding the implementation of a number of articles of the Statistics Law, and the Government's Decree No. 94/2022/ND-CP dated November 7, 2022, prescribing the statistical indicator in the national statistical indicators system, and process of compiling gross domestic product indicators and gross product indicators in provinces and centrally run cities;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 89/2022/ND-CP dated October 28, 2022, defining the functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Planning and Investment;
At the proposal of the Director General of the General Statistics Office;
The Minister of Planning and Investment hereby promulgates the Circular on the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam.
Article 1. Scope of regulation and subjects of application
1. This Circular regulates the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam, including:
a) List of statistical indicators for sustainable development of Vietnam specified in Appendix I to this Circular, including 145 statistical indicators, which reflect 17 sustainable development objectives of Vietnam;
b) Contents of statistical indicators for sustainable development of Vietnam specified in Appendix II to this Circular, including definitions, calculation methods; main groups; publication periods; data sources and agencies responsible for collection and synthesis.
2. The Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam is a set of statistical indicators related to many sectors, fields, and regional linkages to provide data to assess the implementation of Vietnam's sustainable development objectives.
3. This Circular applies to agencies, organizations and individuals providing, producing and using statistical information for Vietnam's sustainable development objectives.
Article 2. Implementation organization
1. The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office) shall assume the prime responsibility for, and coordinate with relevant agencies in:
a) Collecting and summarizing statistical information of the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam, ensuring to provide statistical data on a sufficient, accurate and timely manner to meet the international comparison requirements;
b) Developing and completing forms of collecting information of the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam;
c) Developing the database of sustainable development statistics of Vietnam and disseminating statistical information on sustainable development statistical indicators of Vietnam.
2. Ministries, ministerial-level agencies, government-attached agencies, the Supreme People's Court, Supreme People’s Procuracy, and relevant agencies shall, based on the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam, collect, summarize and compile assigned indicators and provide them to the Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office) for general synthesis.
Article 3. Effect
1. This Circular takes effect from March 10, 2025.
2. Circular No. 03/2019/TT-BKHDT dated January 22, 2029, of the Minister of Planning and Investment, on the Set of Statistical Indicators for Sustainable Development of Vietnam, ceases to be effective from the effective date of this Circular.
3. Any difficulties arising in the course of implementation should be reported to the Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office) for timely guidance, study, amendment and supplementation./.
|
|
THE MINISTER
Nguyen Chi Dzung |
Appendix I
LIST OF STATISTICAL INDICATORS FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF VIETNAM
(Attached to Circular No. 02/2025/TT-BKHDT dated January 3, 2025, of the Minister of Planning and Investment)
|
No. |
Code |
Corresponding national indicator code |
Goals and targets |
|
Goal 1. Ending poverty in all its forms everywhere. |
|||
|
1 |
1.1.1 |
|
The proportion of population below the international poverty line |
|
2 |
1.2.1 |
1802 |
Multidimensional poverty rate |
|
3 |
1.2.2 |
1803 |
The rate of multidimensionally poor children |
|
4 |
1.3.1.a |
|
The proportion of employees participating in social insurance |
|
5 |
1.3.1.b |
|
The proportion of employees participating in unemployment insurance |
|
6 |
1.3.1.c |
0714. |
The proportion of health insurance participants |
|
7 |
1.3.1.d |
0716. |
The number of social insurance, health insurance and unemployment insurance beneficiaries |
|
8 |
1.3.1.e |
|
The number of people receiving monthly social assistance in the community |
|
9 |
1.3.1.g |
|
The number of people receiving emergency social assistance |
|
10 |
1.3.1.h |
|
The number of people being cared for in social protection establishments and social houses |
|
11 |
1.4.1 |
|
The proportion of population living in households with access to basic services |
|
Goal 2. Ending hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture |
|||
|
12 |
2.1.2 |
0813 |
The proportion of food insecurity |
|
13 |
2.2.1 |
1607 |
The proportion of malnourished children under 5 years old (height for age - stunted) |
|
14 |
2.2.2.a |
1607. |
The proportion of malnourished children under 5 years old (weight-for-height - wasting) |
|
15 |
2.2.2.b |
|
The overweight and obesity rate among children under 5 years old |
|
16 |
2.3.1 |
|
Labor productivity in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
|
17 |
2.3.2 |
|
Average income of workers in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
|
18 |
2.4.1 |
0814 |
The proportion of agricultural production land area achieving efficiency and sustainability |
|
19 |
2.5.1.a |
|
The number of plant genetic resources conserved |
|
20 |
2.5.1.b |
|
The number of animal genetic resources conserved |
|
21 |
2.c.1 |
1101. |
The consumer price index for food and foodstuff groups |
|
Goal 3. Ensuring healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages |
|||
|
22 |
3.1.1 |
1603 |
Maternal mortality ratio per 100,000 live births |
|
23 |
3.1.2 |
|
Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel |
|
24 |
3.2.1 |
1605 |
Under-five mortality rate |
|
25 |
3.2.2.a |
1604. |
Infant mortality rate |
|
26 |
3.3.1.a |
1608. |
Number of HIV infections detected per 100,000 population |
|
27 |
3.3.2 |
|
Number of new tuberculosis (TB) cases per 100,000 population |
|
28 |
3.3.3 |
|
Number of new malaria cases per 100,000 population |
|
29 |
3.5.2 |
|
Percentage of the people aged 15 years and older consuming alcohol at a harmful level |
|
30 |
3.6.1 |
1901 |
Number of traffic accident; number of traffic injuries or deaths |
|
31 |
3.7.1 |
|
The proportion of women aged 15-49 years with the need for family planning using modern contraceptive methods |
|
32 |
3.7.2 |
|
Adolescent birth rate (10 -14 years; 15 -19 years) |
|
33 |
3.8.1 |
|
Coverage of essential health services |
|
34 |
3.8.2 |
|
Percentage of people living in households with large out-of-pocket health expenditures |
|
35 |
3.a.1 |
|
Percentage of the population aged 15 years and over who currently use tobacco product |
|
36 |
3.b.1 |
1606. |
Percentage of children under 1 year old fully vaccinated |
|
37 |
3.c.1 |
|
Number of health workers per 10,000 people |
|
Goal 4. Ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all |
|||
|
38 |
4.1.1 |
1503 |
General school enrollment rate |
|
39 |
4.1.2 |
|
Percentage of students completing primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels |
|
40 |
4.2.2 |
|
Rate of mobilizing 5-year-old children to attend preschools |
|
41 |
4.3.1.a |
1507. |
Number of university students per 10,000 people |
|
42 |
4.3.1.b |
0203. |
Rate of trained workers |
|
43 |
4.4.1 |
1317 |
The proportion of individuals aged 15–64 with information and communication technology (ICT) skills |
|
44 |
4.5.1 |
|
Gender equality index in education across primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels |
|
45 |
4.6.1 |
|
The literacy rate of the population aged 15 and above |
|
46 |
4.7.1 |
|
The proportion of schools providing education on gender, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV awareness |
|
47 |
4.a.1 |
|
The proportion of schools equipped with: (a) electricity; (b) Internet for learning purposes; (c) computers for learning purposes; (d) infrastructure and materials suitable for students with disabilities; (e) drinking water; (f) adequate and gender-specific sanitation facilities; and (g) convenient handwashing facilities |
|
48 |
4.c.1 |
|
The proportion of teachers meeting or exceeding the standard training level |
|
Goal 5. Achieving gender equality and empower all women and girls |
|||
|
49 |
5.1.1.a |
0103. |
Sex ratio at birth |
|
50 |
5.2.1 |
|
The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months |
|
51 |
5.2.2 |
|
The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the previous 12 months |
|
52 |
5.3.1 |
|
The proportion of women aged 20 - 24 who were first married or in union before age 15 or 18 |
|
53 |
5.3.1.a |
|
The proportion of child marriages |
|
54 |
5.4.1 |
|
The proportion of time spent on unpaid domestic and care work |
|
55 |
5.5.1.a |
0211. |
The proportion of women in the National Assembly |
|
56 |
5.5.1.b |
0212. |
The proportion of women in People's Councils |
|
57 |
5.5.2 |
|
The proportion of women in leadership positions across sectors, levels, and units |
|
58 |
5.6.1 |
|
The proportion of women aged 15 - 49 who make their own decisions on sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care |
|
59 |
5.a.1 |
|
The proportion agricultural land-using households with land use certificates |
|
60 |
5.b.1 |
|
The proportion of individuals owning mobile phones |
|
Goal 6. Ensuring availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all |
|||
|
61 |
6.1.1 |
1808 |
The proportion of population using safely managed drinking water source |
|
62 |
6.2.1 |
1809 |
The proportion of population using safely managed sanitation facilities |
|
63 |
6.3.1 |
|
The proportion of urban wastewater collected and treated according to standards and regulations |
|
64 |
6.3.1.a |
|
The proportion of operating industrial zones with centralized wastewater treatment systems meeting environmental standards |
|
65 |
6.4.1.a |
|
The proportion of large reservoirs monitored and controlled to ensure the maintenance of minimum river basin flows |
|
66 |
6.4.1.b |
|
The proportion of large and important reservoirs on river basins operated according to inter-reservoir coordination regulations |
|
67 |
6.6.1.a |
|
The number of Ramsar sites established and recognized |
|
Goal 7. Ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all |
|||
|
68 |
7.1.1 |
|
The proportion of the population with access to electricity |
|
69 |
7.1.2 |
|
The proportion of households using clean fuels |
|
70 |
7.2.1 |
|
The share of renewable energy in total final energy consumption |
|
71 |
7.3.1.a |
|
Total primary energy supply per GDP |
|
72 |
7.3.1.b |
|
Energy intensity per gross domestic product (GDP) |
|
73 |
7.b.1 |
|
Installed capacity of renewable energy |
|
Goal 8. Promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all |
|||
|
74 |
8.1.1 |
|
The growth rate of GDP per capita |
|
75 |
8.1.1.b |
0503. |
The growth rate of gross domestic product (GDP) |
|
76 |
8.2.1 |
|
The growth rate of labor productivity |
|
77 |
8.3.1 |
0206 |
The proportion of workers in informal employment |
|
78 |
8.5.1 |
0209 |
The average income per employed worker |
|
79 |
8.5.2 |
0204 |
The unemployment rate |
|
80 |
8.6.1 |
|
The proportion of youth aged 15 - 24 not in employment, education, or training (NEET) |
|
81 |
8.7.1 |
0207 |
The proportion of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor |
|
82 |
8.8.1 |
|
The number of work-related injuries |
|
83 |
8.9.1 |
|
The contribution of tourism activities to GDP |
|
84 |
8.10.1 |
|
The number of commercial bank branches and ATMs per 100,000 population aged 15 and above |
|
85 |
8.10.2 |
0707 |
The proportion of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions |
|
Goal 9. Building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation |
|||
|
86 |
9.1.2.a |
1202. |
Number of passenger trips transported and transited |
|
87 |
9.1.2.b |
1203. |
Volume of goods transported and transited |
|
88 |
9.2.1.a |
|
Share of added value in the manufacturing and processing industry within the GDP |
|
89 |
9.2.1.b |
0904. |
Per capita added value in the manufacturing and processing industry at purchasing power parity |
|
90 |
9.2.2 |
|
Share of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry |
|
91 |
9.3.2 |
|
Number of small- and medium-sized enterprises with outstanding loans at credit institutions |
|
92 |
9.5.1 |
1406 |
Spending on scientific research and technology development relative to GDP |
|
93 |
9.5.2 |
1403 |
Number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development per 1,000,000 population |
|
94 |
9.c.1 |
1314. |
Proportion of the population covered by mobile networks |
|
95 |
9.c.2 |
|
Proportion of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access |
|
Goal 10. Reducing inequality within and among societies |
|||
|
96 |
10.1.1.a |
|
Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita income growth rate |
|
97 |
10.1.1.b |
|
Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita expenditure growth rate |
|
98 |
10.2.1 |
|
Proportion of people living below 50% of the median income |
|
99 |
10.4.1 |
|
Share of labor value in the GDP |
|
100 |
10.4.2 |
1805 |
Gini coefficient of income distribution inequality |
|
101 |
10.7.1 |
|
Recruitment cost ratio paid by migrant workers relative to their monthly income in destination countries |
|
Goal 11. Developing sustainable, resilient urban and rural areas; ensuring safe living and working environments; and rationally distributing populations and labor across regions |
|||
|
102 |
11.1.1 |
|
Proportion of the population living in temporary housing |
|
103 |
11.5.1 |
2103 |
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people |
|
104 |
11.5.2 |
2103 |
Total economic losses caused by natural disasters |
|
105 |
11.6.1 |
2107 |
Proportion of urban solid waste collected and treated |
|
106 |
11.8.1 |
|
Proportion of communes recognized as meeting new rural standards |
|
107 |
11.8.2 |
2107 |
Proportion of rural solid waste collected and treated |
|
Goal 12. Ensuring sustainable production and consumption patterns |
|||
|
108 |
12.4.2 |
2106 |
Proportion of hazardous waste collected and treated |
|
109 |
12.4.3 |
|
Proportion of polluted land areas remediated, rehabilitated, and restored according to regulations |
|
Goal 13. Taking timely, effective action against climate change and natural disasters |
|||
|
110 |
13.1.1 |
2103 |
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people |
|
111 |
13.2.2 |
2110 |
Per capita greenhouse gas emissions |
|
112 |
13.3.1.a |
|
Proportion of greenhouse gas-emitting facilities with emission reduction plans implemented |
|
113 |
13.3.2 |
|
Proportion of the population educated on disaster prevention and control |
|
Goal 14. Conserving and sustainably using oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development |
|||
|
114 |
14.1.1.a |
|
Proportion of coastal water monitoring points meeting national technical standards for organic pollution (N-NH4+) and mineral oil |
|
115 |
14.5.1 |
|
Proportion of marine and coastal protected areas relative to the total national marine area |
|
Goal 15. Protecting and sustainably developing forests, conserving biodiversity, enhancing ecosystem services, combating desertification, preventing degradation, and restoring land resources |
|||
|
116 |
15.1.1 |
2102 |
Forest coverage ratio |
|
117 |
15.1.2 |
|
Proportion of terrestrial protected areas relative to the total territorial land area |
|
118 |
15.2.1.a |
|
Area of forests under protection |
|
119 |
15.3.1 |
2105 |
Proportion of degraded land area |
|
120 |
15.6.1 |
|
Proportion of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge |
|
121 |
15.6.2 |
|
Number of applications for access to genetic resources and benefit-sharing |
|
Goal 16. Promoting peaceful, just, and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all, and building accountable and participatory institutions at all levels. |
|||
|
122 |
16.1.1 |
|
Number of victims of intentional homicide per 100,000 people |
|
123 |
16.1.3 |
1905 |
Proportion of the population affected by violence |
|
124 |
16.1.4 |
|
Proportion of the population feeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark |
|
125. |
16.2.1 |
|
The proportion of individuals under 18 who have experienced physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month |
|
126 |
16.2.2 |
|
Number of victims of human trafficking detected per 100,000 people |
|
127 |
16.2.3 |
|
Proportion of individuals aged 18-29 who experienced sexual violence before the age of 18 |
|
128 |
16.3.1 |
|
Proportion of victims of violence in the past 12 months who reported the incident to competent authorities or supportive organizations |
|
129 |
16.4.2 |
|
Total number of confiscated illegal weapons, explosives, and support tools |
|
130 |
16.5.1 |
|
Proportion of individuals paying informal costs to access public services |
|
131 |
16.5.2 |
|
Proportion of businesses paying informal costs to access public services |
|
132 |
16.6.1 |
|
Proportion of public budget expenditure compared to the approved budget estimate |
|
133 |
16.6.2 |
|
Proportion of population satisfied with their last experience of public services |
|
134 |
16.9.1 |
0113 |
Proportion of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered |
|
Goal 17. Strengthening the means of implementation and revitalizing the global partnership for sustainable development |
|||
|
135 |
17.1.1 |
0602 |
Total state budget revenue as a proportion of GDP |
|
136 |
17.1.2 |
|
Proportion of domestic budget funded by domestic taxes |
|
137 |
17.3.1.a |
|
Official development assistance and concessional loans of foreign donors |
|
138 |
17.3.1.b |
|
Foreign direct investments in Vietnam |
|
139 |
17.4.1 |
|
National external debt service as a proportion of exports of goods and services |
|
140 |
17.6.1 |
1307 |
Number of broadband Internet subscriptions per 100 inhabitants |
|
141 |
17.8.1 |
1306 |
Proportion of individuals using the Internet |
|
142 |
17.11.1 |
1006 |
Value of exports and imports |
|
143 |
17.17.1 |
|
Total number of public-private partnership investment projects |
|
144 |
17.19.1 |
|
Proportion of birth registrations |
|
145 |
17.19.2 |
|
Proportion of death registrations |
Appendix II
CONTENTS OF STATISTICAL INDICATORS FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF VIETNAM
(Attached to Circular No. 02/2025/TT-BKHDT dated January 3, 2025, of the Minister of Planning and Investment)
Goal 1. Ending poverty in all its forms everywhere.
1.1.1. Proportion of population below the international poverty line
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of the population below the international poverty line is the percentage of people whose daily income is less than US$2.15 (2017 purchasing power parity) compared to the total population at the time.
Formula:
|
The proportion of population below the international poverty line (%) |
= |
The population whose average daily income is below US$2.15 in 2017 (2017 purchasing power parity) |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
1.2.1. Multidimensional poverty rate
1. Definition, calculation method
The multidimensional poverty rate refers to the percentage of households classified as multidimensionally poor relative to the total number of households.
Formula:
|
Multidimensional poverty rate (%) |
= |
Number of multidimensionally poor households |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
Criteria for multidimensional poverty include: (1) Income criterion and (2) criterion regarding deprivations in access to basic social services. Criteria for determining multidimensional poverty standards are based on corresponding legal documents for each period.
2. Main disaggregation
- Ethnicity of the head of the household;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
1.2.2. The rate of multidimensionally poor children
1. Definition, calculation method
The rate of multidimensionally poor children refers to the percentage of children aged between 0 and 15 years who are multidimensionally poor compared the total number of children aged between 0 and 15 years.
Formula:
|
The rate of multidimensionally poor children (%) |
= |
Total number of multidimensionally poor children aged 0 -15 |
x 100 |
|
Total number of children aged 0 - 15 |
Based on currently available data, the dimensions of access to basic social services used to identify multidimensional child poverty include education, healthcare, housing, access to hygienic water, access to hygienic sanitation facilities, nutrition, and access to information technology. A child is deemed multidimensionally poor if they lack 2 or more of these basic social service dimensions. Each dimension has corresponding indicators that determine the degree of deprivation.
Note: In the event that the state management agency in charge of child-related matters issues a legal document guiding the criteria for identifying multidimensionally poor children, the calculation method shall be adjusted in accordance with the provisions of such legal document.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
1.3.1.a. Rate of employees participating in social insurance
Social insurance means the guarantee to fully or partially offset an employee’s income that is reduced or lost due to his/her sickness, maternity, labor accident, occupational disease, retirement or death, on the basis of his/her contributions to the social insurance fund.
The number of persons participating in social insurance includes individuals participating in compulsory social insurance and those participating in voluntary social insurance.
Compulsory social insurance means a form of social insurance organized by the State in which employees and employers are required to participate.
Voluntary social insurance means a form of social insurance organized by the State in which a participant may select a premium rate and a method of premium payment suitable to his/her income and the State supports his/her payment of social insurance premiums for him/her to enjoy retirement and survivorship allowance regimes.
The number of persons participating in compulsory social insurance covers the following categories:
- Employees being Vietnamese citizens covered by compulsory social insurance, including:
+ Persons working under indefinite-term labor contracts, definite-term labor contracts with a term of one month or more, including cases where the employees and employers agree on a different name but with content showing paid work, salary and management, operation and supervision by one party;
+ Cadres, civil servants and public employees;
+ Defense workers and employees, public security workers and persons doing other jobs in cipher organizations;
+ Officers and professional army men of the people’s army; officers and professional non-commissioned officers and officers and technical non-commissioned officers of the people’s public security; and persons engaged in cipher work and enjoying salaries like army men;
+ Non-commissioned officers and soldiers of the people’s army; non-commissioned officers and soldiers on duty in the people’s public security; army, public security and cipher cadets who are entitled to cost-of-living allowance;
+ Standing militia;
+ Vietnamese guest workers as prescribed in the Law on Vietnamese Guest Workers, unless otherwise specified by treaties to which the Socialist Republic of Vietnam is a contracting party;
+ Spouses not entitled to salary from the state budget who are sent on a term of office with a member of an overseas representative mission of Vietnam abroad with living allowance;
+ Salaried managers of enterprises, controllers, representatives of state capital, representatives of enterprise capital as prescribed by law; salaried members of the Board of Directors, General Directors, Directors, members of the Board of Supervisors or controllers and other elected management positions of cooperatives and cooperative unions as prescribed by the Law on Cooperatives;
+ Persons working on a part-time basis in communes, villages and residential quarters;
+ Persons specified at Point a of this Clause who work part-time and have monthly salary equal to or higher than the lowest salary on which compulsory social insurance premiums are based;
+ Business household owners of business households with business registration who participate in insurance in accordance with the Government's regulations;
+ Non-salaried corporate managers, controllers, representatives of state capital, representatives of enterprise capital as prescribed by law; non-salaried members of the Board of Directors, General Directors, Directors, members of the Board of Supervisors or controllers and other elected management positions of cooperatives and cooperative unions as prescribed by the Law on Cooperatives.
- Workers who are foreign citizens working in Vietnam shall be covered by compulsory social insurance if they work for a Vietnamese employer under a definite-term labor contracts with a term of 12 months or more.
- Employers covered by compulsory social insurance include state agencies, public non-business units; and people’s armed forces and public security units, agencies and enterprises, cipher organizations; political organizations, socio-political organizations, socio-politico-professional organizations, socio-professional organizations and other social organizations; foreign agencies and organizations, and international organizations operating in the Vietnamese territory; enterprises, cooperatives, individual business households, cooperative groups, cooperatives, cooperative unions, business households and other organizations and individuals that hire or employ employees under labor contracts.
Persons participating in voluntary social insurance are Vietnamese citizens aged full 15 years or older who are not covered compulsory social insurance, other than those who are entitled to pensions, social insurance allowance and monthly allowance.
The rate of employees participating in social insurance is the percentage of social insurance participants compared to the labor force of working age in the reporting year.
Formula:
|
The rate of employees participating in social insurance (%) |
= |
Number of social insurance participants in the reporting year |
x 100 |
|
Working-age labor force in the reporting year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Number of social insurance participants: administrative data from Vietnam Social Security;
- Working-age labor force: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: Vietnam Social Security (provide data on the number of social insurance participants).
1.3.1.b. Rate of employees participating in unemployment insurance
1. Concepts, calculation methods
Unemployment insurance means a scheme aiming to compensate part of income of a worker when he/she becomes unemployed, support him/her to receive vocational training, maintain employment, or seek employment, on the basis of making contributions to the Unemployment Insurance Fund.
The number of employees participating in unemployment insurance is determined as follows:
- Workers are obliged to participate in unemployment insurance when working under labor contracts or working contracts below:
+ Labor contracts or working contracts of indefinite time;
+ Labor contracts or working contracts of definite time.
In case a worker has signed and is performing more than one labor contract, the worker and the employer under the labor contract signed first shall participate in unemployment insurance.
- Workers defined in Clause 1 Article 43 of the Law on Unemployment who are currently on pension or doing housework are not required to participate in unemployment insurance.
- Employers obliged to participate in unemployment insurance include state agencies, public non-business units and people’s armed forces units; political organizations, socio-political organizations, socio-political-professional organizations, social organizations and socio-professional organizations; foreign agencies and organizations and international organizations operating in the Vietnamese territory; enterprises, cooperatives, households, business households, cooperative groups, other organizations and individuals that hire or employ workers under the labor contracts or working contracts.
The rate of employees participating in unemployment insurance is the percentage of the total number unemployment insurance participants compared to the labor force of working age in the reporting year.
Formula:
|
The rate of employees participating in unemployment insurance (%) |
= |
Number of unemployment insurance participants in the reporting year |
x 100 |
|
Working-age labor force in the reporting year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Number of unemployment insurance participants: administrative data from Vietnam Social Security;
- Working-age labor force: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs; Vietnam Social Security (provide data on the number of unemployment insurance participants).
1.3.1.c. Rate of health insurance participants
1. Concepts, calculation methods
a) The number of health insurance participants
Health insurance is a form of compulsory insurance applied to target groups prescribed in the Law on Health Insurance for healthcare and non-profit purposes, the implementation of which is organized by the State.
The number of health insurance participants is determined according to 6 specific participant groups, as follows:
- Persons whose health insurance premiums are paid by employees and employers;
- Persons whose health insurance premiums are paid by social security agencies;
- Persons whose health insurance premiums are paid by the state budget;
- Persons whose health insurance premiums are paid with the state budget support;
- Persons participating in household-based health insurance;
- Persons whose health insurance premiums are paid by employers.
Details on persons who participate in health insurance within these 6 groups are stipulated in Articles 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 Chapter I of the Government’s Decree No. 146/2018/ND-CP dated October 17, 2018, detailing, and guiding measures to implement, a number of articles of the Law on Health Insurance.
b) The rate of health insurance participants
The rate of health insurance participants is the percentage of the total number of health insurance participants compared to the average population in the reporting year.
Formula:
|
The rate of health insurance participants (%) |
= |
Number of health insurance participants in the reporting year |
x 100 |
|
Average population in the reporting year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Group of health insurance participants;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- The number of health insurance participants: administrative data from Vietnam Social Security;
- Average population: Population and family planning change survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: Vietnam Social Security (collect data on the number of health insurance participants).
1.3.1.d. The number of social insurance, health insurance and unemployment insurance beneficiaries
1. Definition, calculation method, and main disaggregation
a) Number of persons covered by social insurance fund
The number of persons covered by social insurance fund is the count of individuals who have participated in social insurance and have received social insurance payments (calculated by person, irrespective of whether one person may receive multiple different social insurance benefits).
The number of persons receiving social insurance payments is disbursed under the following benefit categories: sickness and maternity; occupational accidents and diseases; retirement; and survivors’ benefits.
Main disaggregation
- Type of benefit;
- Payment duration (one-time/monthly);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
a) The number of persons receiving health insurance
The number of persons receiving health insurance is the count of individuals who participate in health insurance and receive health insurance-covered healthcare services when seeking medical treatment (calculated by the number of patient visits covered by health insurance).
Main disaggregation
- Form of treatment (inpatient/outpatient);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
c) Number of persons receiving unemployment insurance
The number of persons receiving unemployment insurance is the count of individuals who have paid unemployment insurance premiums and, upon losing their jobs (unemployment), receive unemployment insurance benefits (calculated by the number of persons receiving unemployment benefits).
Main disaggregation
- Type of support (unemployment benefits/vocational training support/training support for skill enhancement);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
2. Publication frequency Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data from Vietnam Social Security.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: Vietnam Social Security.
1.3.1.e. Number of people receiving monthly social assistance in the community
1. Definition, calculation method
Persons eligible for monthly social allowances include:
1. Children under 16 years old having no nurture source subject to one of the cases prescribed as follows:
a) Being abandoned and not yet adopted;
b) Being an orphan who has lost both parents;
c) Being an orphan, whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is announced missing as prescribed by law;
d) Being an orphan, whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is receiving the care and nurture benefits at social protection establishments or social houses;
dd) Being an orphan whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
e) Both parents are announced missing as prescribed by law;
g) Both parents are receiving the care and nurture benefits at social protection establishments or social houses,
h) Both parents are serving the prison term in jail or are exercising the decisions on handling of administrative violation at reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
i) The mother or father is announced missing as prescribed by law and the remaining parent is receiving the care and nurture benefits at the social protection establishments or social houses;
k) The mother or father is announced missing as prescribed by law and the remaining parent is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at the reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
l) The mother or father is receiving the care and nurture benefits at the social protection establishments or social houses, and the remaining is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at the reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments.
2. Persons specified in Clause 1 of this Article who are enjoying monthly social allowance, but reach full 16 years of age and are studying in high schools, vocational schools, professional secondary schools, colleges, or universities of first degree, shall continue to enjoy social assistance policies until the end of their education, but not more than the age of 22.
3. Children infected with HIV of poor households.
4. Persons belong to poor or near-poor households who are not married; those who are married but the wife or husband has died or is missing as prescribed by law and they are raising children under 16 years old or children between 16 and 22 years old who are in high schools, vocational schools, professional secondary schools, colleges or universities of first degree as prescribed in Clause 2 of this Article (hereafter referred to as poor and single persons who are raising children).
5. The elderly subject to one of the following cases:
a) The elderly belonging to poor households who do not have any person with obligations and rights to serve them, or have such persons but they are receiving monthly social allowances;
b) The elderly from full 75 to 80 years old belonging to poor or near-poor households, but not subject to the provisions at Point a of this Clause and living in communes and villages in ethnic minority areas and mountainous areas with special difficulties;
c) The elderly from full 80 years old or older not subject to the provisions at Point a of this Clause, who have no monthly pension, social insurance allowance, or social allowance;
d) The elderly belonging to poor households who do not have any person with obligations and rights to serve them, have no condition to live in community, meet the conditions to be admitted to the social protection establishments or social houses but there are other persons who wish to take care of them in community.
6. Persons with severe disabilities or extremely severe disabilities as prescribed by the law on persons with disabilities.
7. Children under 3 years old belonging to poor or near-poor households other than those specified in Clauses 1, 3 and 6 of this Article, living in communes and villages in ethnic minority areas and mountainous areas with special difficulties.
8. Persons infected with HIV/AIDS belonging to poor households without a stable monthly income source such as salary, wages, pension, social insurance allowance, or monthly social allowance.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Subject groups;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the labor, invalids, and social affairs sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
1.3.1.g. Number of people receiving emergency social assistance
1. Definition, calculation method
Individuals eligible for emergency social allowances include:
+ Households with deceased or missing members due to natural disasters, fires, epidemics, traffic accidents, especially serious occupational accidents, or other force majeure causes;
+ Individuals seriously injured by natural disasters, fires, traffic accidents, especially serious occupational accidents, or other force majeure causes;
+ Poor or near-poor households, or households in difficult circumstances whose dwellings are severely damaged, collapsed, swept away, or completely destroyed by natural disasters, fires, or other force majeure causes such that they have no place to live;
+ Households that must urgently relocate their dwellings under a decision by a competent agency due to the risk of landslides, flooding, natural disasters, fires, or other force majeure causes;
+ Children who have lost both parents, or whose parents have gone missing due to natural disasters, fires, or other force majeure causes, with no relatives available to provide care or support.
2. Main disaggregation
- Subject groups;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the labor, invalids, and social affairs sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
1.3.1.h. Number of people being cared for in social protection establishments and social houses
1. Definition, calculation method
Persons receiving care and support at social protection establishments and social houses include:
1. Social protection subjects with extremely difficult circumstances include:
a) Children in difficult circumstances, who cannot take care of themselves and have no persons admitting them for care and nurture in community, including:
Children under 16 years old having no nurture source subject to one of the cases prescribed as follows:
- Being abandoned and not yet adopted;
- Being an orphan who has lost both parents;
- Being an orphan whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is missing as prescribed by law;
- Being an orphan whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is receiving the care and nurture benefits at social protection establishments or social houses;
- Being an orphan whose mother or father has died, and the remaining parent is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
- Both parents are missing as prescribed by law;
- Both parents are receiving the care and nurture benefits at social protection establishments or social houses;
- Both parents are serving the prison term in jail or are exercising the decisions on handling of administrative violation at reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
- The mother or father is missing as prescribed by law and the remaining parent is receiving the care and nurture benefits at the social protection establishments or social houses;
- The mother or father is missing as prescribed by law and the remaining parent is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at the reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments;
- The mother or father is receiving the care and nurture benefits at the social protection establishments or social houses, and the remaining is serving prison term in jail or is exercising the decision on handling of administrative violation at the reformatories, compulsory educational establishments, or compulsory detoxification establishments.
Children infected with HIV belonging to poor households; persons infected with HIV belonging to poor households who are no longer capable of working and do not receive pensions, monthly social insurance benefits, monthly preferential benefits for persons with meritorious services, or other monthly allowances.
b) The elderly who qualify for care and support at social protection establishments or social houses under the laws on the elderly;
c) Children with disabilities and persons with disabilities who qualify for care and support at social protection establishments or social houses under the law on persons with disabilities.
2. Persons requiring urgent protection, including:
a) Victims of domestic violence; victims of sexual abuse; victims of trafficking; victims of forced labor;
b) Children, vagrants, and homeless beggars when they are waiting to be taken to their places of residence;
c) Other subjects in urgent need of protection under decisions of Chairpersons of provincial-level People’s Committees.
3. Minors and persons who are no longer able to work shall be entitled to care and nurture at social protection establishments in accordance with the law on handling of administrative violations.
4. Persons who voluntarily live at social protection establishments include:
a) The elderly under caregiver contracts;
b) Persons other than those specified in Clauses 1 and 2, who are unable to live at home and wish to live at social protection establishments.
2. Main disaggregation
- Subject groups;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the labor, invalids, and social affairs sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
1.4.1. Percentage of population living in households with access to basic services
1. Definition, calculation method
The rate of population living in households with access to basic services is the percentage of people living in households that have access to basic services out of the total population in a specified year.
Basic services are defined according to the multidimensional poverty standards set in the applicable national poverty standards for each period.
Formula:
|
The rate of population living in households with access to basic services (%) |
= |
Population living in households with access to basic services |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 2. Ending hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
2.1.2. Food insecurity rate
1. Definition, calculation method
Food security is the condition in which everyone has the ability to access sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to maintain a healthy and active life.
This indicator measures the percentage of the population experiencing moderate or severe food insecurity.
Formula:
|
Food insecurity rate (%) |
= |
Population experiencing food insecurity |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
The population experiencing food insecurity is collected and calculated according to the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES) prescribed by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. FIES assesses degrees of food shortages through eight aspects:
|
No. |
FIES items |
|
1 |
Worried about not having enough food |
|
2 |
Unable to afford nutritious and healthy food |
|
3 |
Ate only a few kinds of foods |
|
4 |
Skipped a meal |
|
5 |
Ate less than needed |
|
6 |
Ran out of food |
|
7 |
Became hungry |
|
8 |
Did not eat for an entire day |
Individual- or household-level data are collected using a food security questionnaire in a sample survey.
The methodology used for analyzing FIES data is based on Item Response Theory (IRT). The specific IRT model applied to FIES data is the Rasch model (one-parameter logistic model, 1-PL).
2. Main disaggregation Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
2.2.1. Rate of malnourished children under 5 years old (height for age - stunted)
1. Definition, calculation method
The stunting rate among children under 5 years of age is the percentage of children under 5 whose height-for-age is below minus two standard deviations (-2SD) from the median height of the World Health Organization (WHO) reference population.
The WHO reference population is a group of children in good health, with normal weight and height growth. Their weight and height are used by the WHO as standards to assess the nutritional status of children in the same age group. The WHO 2006 reference population replaces previous ones from the United States and earlier WHO reference populations.
Nutritional status is classified into the following levels:
- Normal: ≥ - 2SD
- Malnourished:
Grade I (mild): < - 2SD and ≥ - 3SD
Grade II (severe): < - 3SD and ≥ - 4SD
Grade III (very severe): < - 4SD
In which SD is the standard deviation.
Formula:
|
Stunting rate among children under 5 (%) |
= |
Number of children under 5 years of age with height-for-age stunting |
x 100 |
|
Number of children under 5 measured for height |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity (Kinh/other);
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Nutrition survey
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
2.2.2.a. The proportion of malnourished children under 5 years old (weight-for-height - wasting)
1. Definition, calculation method
The wasting rate among children under 5 years of age is the percentage of children under 5 whose weight-for-height is below minus two standard deviations (-2SD) from the median height of the World Health Organization (WHO) reference population.
The WHO reference population is a group of children in good health, with normal weight and height growth. Their weight and height are used by the WHO as standards to assess the nutritional status of children in the same age group. The WHO 2006 reference population replaces previous ones from the United States and earlier WHO reference populations.
|
Wasting rate among children under 5 years of age (%) |
= |
Number of children under 5 years of age with height-for-height wasting |
x 100 |
|
Number of children under 5 weighed and measured for height |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity (Kinh/other);
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Nutrition survey
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
2.2.2.b. The overweight and obesity rate among children under 5 years old
1. Definition, calculation method
The overweight and obesity rate among children under 5 is calculated by taking the total number of children under 5 who are overweight or obese relative to the total number of children under 5 who are weighed and measured in a given locality (province/district/commune) at the time of the survey.
Assessment of overweight and obesity for children under 5 is based on the Z-score of weight-for-height. Under the WHO reference population 2006, overweight/obesity among children under 5 is classified according to the following weight-for-height Z-score thresholds (WHZ):
Weight-for-Height Z-score (WHZ):
|
1 < Z-score ≤ 2 |
Risk of overweight |
|
2 < Z-score ≤ 3 |
Overweight |
|
Z-score > 3 |
Obesity |
Formula:
|
The overweight and obesity rate among children under 5 years old (%) |
= |
Number of children under 5 who are overweight or obese |
x 100 |
|
Total number of children under 5 weighed and measured |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity (Kinh/other);
- Urban/rural/mountainous area;
- Province/city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Nutrition survey
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
2.3.1. Labor productivity in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector
1. Definition, calculation method
Labor productivity in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector reflects the working efficiency of the labor force in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector, and is typically measured by the sector’s gross domestic product (GDP) per employed person over the reference period.
Formula:
|
Labor productivity in the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
= |
GDP of agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
|
Total number of employed persons in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
2. Publication frequency Annually.
3. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
2.3.2. Average income of employed persons in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector
1. Definition, calculation method
Income of employed persons in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries includes the following:
- Income from wages, salaries, and other wage-like compensation, including overtime pay, bonuses, allowances, etc., for wage earners in the economy. These incomes may be in cash or in kind.
- Income from production and business activities, consisting of profits derived from agricultural production for sale, or profits from trading goods or services, etc. This does not include income from interest on loans or dividends unrelated to one’s current job.
The average income of an employed person in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries is the total income of all such employed persons compared to the total number of employed persons in the sector.
Formula:
|
Average income of an employed person in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
= |
Total income of all employed persons in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries |
|
Total number of employed persons in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector |
2. Main disaggregation Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
2.4.1. The proportion of agricultural production land area achieving efficiency and sustainability
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of agricultural production land area achieving efficiency and sustainability is the ratio of the area of agricultural land deemed effective and sustainable to the total area of agricultural land;
Formula:
|
The percentage of agricultural production land area achieving efficiency and sustainability (%) |
= |
Area of agricultural land deemed effective and sustainable |
x 100 |
|
Total agricultural land area |
Agricultural land includes land for annual crops and land for perennial crops. Annual crop land includes land for rice cultivation and land for other annual crops.
This indicator is calculated based on sample survey results, using 11 component indicators corresponding to 11 topics in three dimensions (economic, social, and environmental).
|
Dimension |
Topic |
Component indicator |
|
Economy |
Land productivity |
Product value per hectare |
|
Profitability |
Net income |
|
|
Adaptive capacity and resilience |
Risk-mitigation mechanism |
|
|
Environment |
Soil health |
Proportion of land degradation |
|
Water use |
Stability of irrigation water sources |
|
|
Fertilizer pollution risk |
Fertilizer usage |
|
|
Pesticide pollution risk |
Pesticide usage |
|
|
Biodiversity |
Adoption of measures supporting biodiversity in agriculture |
|
|
Social |
Decent work |
Agricultural wages/salaries |
|
Food security |
Food security based on the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES) |
|
|
Land use right |
Assurance of land use right |
The percentage of agricultural land that is effective and sustainable is determined for each component indicator and classified into three levels: high, acceptable, and unsustainable, based on data aggregated at the farm level (where a farm is any entity using agricultural land during the reference period, including households, cooperatives, enterprises, etc.). The sum of the proportions for high, acceptable, and unsustainable for each component indicator is 100%.
The percentage of agricultural land that is effective and sustainable (SDG 2.4.1) equals the combined proportion of land classified as high and acceptable for the component indicator having the lowest combined proportion of high and acceptable results among the 11 component indicators. Formula:
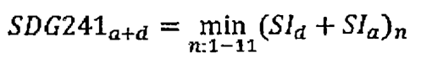
In which:
SDG241a+d: Percentage of agricultural land that is effective and sustainable.
SId: Percentage of agricultural land at a high level of effectiveness and sustainability for the nth component indicator.
Sla: Percentage of agricultural land at an acceptable level of effectiveness and sustainability for the nth component indicator.
n: Number of component indicators.
Calculation of the percentage of agricultural land deemed effective and sustainable for each component indicator:
The denominator for all component indicators is the total agricultural land area of the farms in the sample list.
The numerator for each component indicator, by each level of effectiveness and sustainability (high, acceptable, unsustainable), is the total agricultural land area of the farms (in the sample list) that are classified accordingly. Each farm is classified based on the criteria of each component indicator.
Formula:
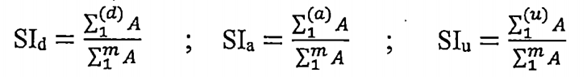 In which:
In which:
Sld; Sla; SIu : are the percentages of agricultural land that are high-level, acceptable-level, or unsustainable, respectively;
m: is the number of farms in the sample survey;
d,a,u: refer to the number of farms classified as high, acceptable, or unsustainable (d+a+u = m);
A: is the area of agricultural land for each farm.
The classification criteria for effectiveness and sustainability are based on the methodology developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Specifically:
|
No. |
Component indicator |
Criteria for efficient and sustainable production (Criteria for classifying sustainable performance at farm level) |
|||||
|
1 |
Product value per hectare |
Each farm calculates its product value per a hectare of agricultural production land, forming a data series on product value per hectare, and then find the value corresponding to the 90th percentile of that series of data. Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: Product value per unit of farm area ≥ 2/3 of the 90th percentile value; Acceptable: Product value per unit of farm area ≥ 1/3 but < 2/3 of the 90th percentile value; Unsustainable: Product value per unit of farm area < 1/3 of the 90th percentile value. Reference period: The year immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
2 |
Net income |
Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: Over three consecutive years, the farm’s agricultural activities show a profit in all three years. Acceptable: Over three consecutive years, the farm’s agricultural activities show a profit in one or two of those years. Unsustainable: Over three consecutive years, the farm’s agricultural activities do not show a profit in any year. Reference period: 3 years immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
3 |
Risk-mitigation mechanism |
This component indicator measures the following risk-mitigation mechanisms: - Access to credit; - Access to insurance; - Diversification in farm production (the proportion of any single agricultural product does not exceed 66% of the total agricultural production value of the farm). Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: The farm meets any 2 of these 3 mechanisms; Acceptable: The farm meets 1 mechanism; Unsustainable: The farm does not meet any mechanism. Reference period: The year immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
4 |
Proportion of land degradation |
This component indicator measures the proportion of agricultural land degraded by issues such as soil erosion, reduction in soil fertility, salinization, drought, pollution, or loss of soil biodiversity, etc. as reported by the farm based on actual production conditions.
Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: Proportion of land degradation < 10% Acceptable: Proportion of land degradation ≥ 10% and < 50% Unsustainable: Proportion of land degradation ≥ 50% Reference period: 3 years immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
5 |
Stability of irrigation water sources |
This component indicator evaluates water source stability from three perspectives: The proportion of irrigated agricultural land; the decline in groundwater, river, and stream levels; and the effectiveness of irrigation water distribution, as assessed by farms based on actual production conditions. Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: Irrigation water sources remain stable over the years; Acceptable: Irrigation water sources are not stable over the years or the stability is uncertain, but there is an organized system for distributing water sufficient to meet irrigation needs. Unsustainable: Other remaining cases. Reference period: 3 years immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
6 |
Fertilizer usage |
This component indicator evaluates the risk of fertilizer-related pollution using a set of “measures to mitigate the environmental impacts of fertilizer,” as assessed by farms based on actual production conditions. Farm classification: High: The farm implements at least four measures to mitigate the risk of environmental pollution; Acceptable: The farm implements 2-3 measures to mitigate the risk of environmental pollution; Unsustainable: The farm implements only one measure or does not implement any measures to mitigate the risk of environmental pollution. Reference period: The year immediately preceding the survey year. |
|||||
|
7 |
Pesticide usage |
This component indicator assesses the risk of pesticide pollution through a set of criteria on “Measures to mitigate the health impacts of pesticides” and “Measures to mitigate the environmental impacts of pesticides,” based on the farm assessments. Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: The farm fully complies with all 3 health-related measures and at least 4 environment-related measures; Acceptable: The farm implements 2 or 3 health-related measures and 2 or 3 environment-related measures; Unsustainable: The farm implements only 1 measure or none at all for health, and only 1 measure or none at all for the environment. Reference period: The year immediately preceding the survey year |
|||||
|
8 |
Adoption of measures supporting biodiversity in agriculture |
This component indicator measures effectiveness and sustainability of biodiversity in production based on five criteria: - At least 10% of the area is left for natural or diverse vegetation; - The farm produces certified organic agricultural products or its products are undergoing the certification process; - The farm does not use medically important antimicrobials as growth promoters; - At least two product groups each account for 10% or more of the total production; - Crop rotation is practiced on at least 80% of the farm’s cultivated area over a 3-year period (excluding perennial crops and permanent grassland); - Use of purebred seeds. Classifying sustainable performance at farm level: High: Meets 3 or more of these criteria; Acceptable: Meets 2 criteria; Unsustainable: Does not meet any criteria. |
|||||
|
9 |
Agricultural wages/salaries |
Farm classification: High: The farm pays wages/salaries exceeding the national minimum wage or the minimum wage for the agricultural sector; Acceptable sustainability: The farm pays wages/salaries equal to the national minimum wage or the minimum wage for the agricultural sector; Unsustainable: The farm pays wages/salaries below the national minimum wage or the minimum wage for the agricultural sector. |
|||||
|
10 |
Food insecurity experience scale (FIES) |
This component indicator assesses farm-level effectiveness and sustainability based on the food insecurity experience of farm members according to the FIES scale and classification. High: The farm experiences no food insecurity or only mild food insecurity; Acceptable: The farm experiences moderate food insecurity; Unsustainable: The farm experiences severe food insecurity. |
|||||
|
11 |
Assurance of land use right |
This component indicator assesses effectiveness and sustainability at the farm level based on four criteria: - Lawful documents of agricultural production land; - Names of farm members stated on the lawful documents (with right or joint right of land ownership or land use right); - Right to sell; - Right to inherit. Farm classification: High: There is legal document with the name of the owner or land user on it, or there is a right to sell any agricultural land parcel, or a right to inherit any agricultural land parcel. Acceptable: There is legal document even if the farm members are not listed as owners or land users. Unsustainable: Other remaining cases. |
2. Disaggregation
- Component indicator;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Rural, agricultural and fishery census;
- Mid-term rural and agricultural survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
2.5.1.a. The number of plant genetic resources conserved
1. Definition, calculation method
Genetic resources are species or genetic specimens within conservation areas, biodiversity conservation facilities, scientific research and technology development institutions, or found in nature.
Plant variety is a population of cultivated plants distinguishable from other plant populations by at least one heritable trait and capable of passing that trait to subsequent generations; it exhibits morphological uniformity and remains stable through multiple propagation cycles, and has agronomic and utilitarian value.
Plant genetic resources are living crop varieties or their genetic specimens capable of creating or contributing to the creation of new plant varieties.
In-situ conservation refers to the conservation of wild species within their natural habitats and the preservation of plant species of value in the environment where their distinctive characteristics evolved and developed.
Ex-situ conservation involves the conservation of wild species outside their regular or seasonal natural habitats and the preservation of valuable plant species outside the environment where their unique traits developed. This method also includes the storage and preservation of genetic resources and genetic specimens in scientific and technological institutions or genetic resource preservation facilities.
Common methods of ex-situ conservation for plant genetic resources include:
- Seed gene banks (stored in cold storage facilities);
- Field gene banks (maintained in agricultural fields);
- In-vitro gene banks (stored in test tubes or glass containers).
The storage duration of genetic resources in cold storage is typically classified as:
+ Long-term storage: 50-100 years, depending on storage conditions and facilities;
+ Medium-term storage: 10-15 years, depending on storage conditions and facilities.
Calculation method: Statistical compilation of the number of conserved and stored plant genetic resources at conservation and plant resource preservation facilities.
2. Main disaggregation
- Name of genetic resource;
- Storage duration (cold storage): Medium-term, long-term.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in agriculture and rural development sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
2.5.1.b. The number of animal genetic resources conserved
1. Definition, calculation method
Livestock breed is a population of animals of the same species and origin, sharing similar external appearance and genetic structure, formed, reinforced, and developed under human influence, with sufficient quantity to allow breeding, capable of transmitting its breed-specific characteristics to subsequent generations (Clause 9 Article 2 of the 2018 Law on Animal Husbandry).
Livestock genetic resources are living animals or their reproductive materials containing genetic information capable of creating or contributing to new livestock breeds (Clause 21 Article 2 of the 2018 Law on Animal Husbandry).
In-situ conservation refers to the conservation of wild species within their natural habitats and the preservation of endemic or valuable livestock in the environment where their distinctive characteristics evolved and developed.
Ex-situ conservation involves the conservation of wild species outside their regular or seasonal natural habitats and the preservation of endemic or valuable livestock outside the environment where their characteristics evolved; storage and preservation of genetic resources and genetic specimens at scientific and technological institutions or genetic resource preservation facilities.
The storage duration of genetic resources in cold storage is typically classified as:
+ Long-term storage: 50-100 years, depending on storage conditions and facilities;
+ Medium-term storage: 10-15 years, depending on storage conditions and facilities.
Calculation method: The total number of livestock genetic resources conserved by organizations or individuals that maintain livestock breeds.
2. Main disaggregation
- Form of conservation;
- Storage duration: Medium-term, long-term.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in agriculture and rural development sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
2.c.1. The consumer price index for food and foodstuff groups
1. Definition, calculation method
The consumer price index (CPI) for food and foodstuffs is a relative indicator (expressed in %) that reflects the trend and extent of overall price fluctuations over time for daily food items consumed by the population.
The representative basket of goods comprises key food and foodstuff items reflecting the consumption patterns of the population over a given period. This basket is used for periodic price surveys to support the calculation of the CPI.
The weighting used in the CPI calculation is the proportion of expenditures on food and foodstuffs in the total household expenditures of the base year. This weight remains fixed for five years.
Every five years, the representative basket of goods and their weights are updated to reflect current consumer markets and spending structures for daily living in the current period.
Formula:
The CPI for food and foodstuffs is calculated using a weighted geometric Laspeyres formula in its general form:
In which:
![]() : is the CPI in the reporting period (t) compared to the fixed base period (0);
: is the CPI in the reporting period (t) compared to the fixed base period (0);
![]() : are prices in the reporting period (t) and the fixed base period (0);
: are prices in the reporting period (t) and the fixed base period (0);
![]() : is the weight in the fixed base period (0);
: is the weight in the fixed base period (0);
![]() : Consumer expenditure in the fixed base period (0).
: Consumer expenditure in the fixed base period (0).
n : is the number of items.
Method for calculating the CPI for food and foodstuffs
The CPI for food and foodstuffs is calculated from consumer price surveys in each province or centrally run city. It is calculated using the weighted geometric mean method, incorporating the price variations of different product groups with their respective weights.
The CPI for food and foodstuffs in provinces and centrally run cities is determined by applying the weighted geometric mean method to the CPI of each surveyed food and foodstuff group, using the corresponding weight coefficients.
The CPI for food and foodstuffs across the six economic regions is calculated using the weighted geometric mean method, aggregating the CPI for food and foodstuffs from each province and centrally run city within the respective region, applying the corresponding weight coefficients.
The national CPI for food and foodstuffs is calculated as the weighted geometric mean of the CPI for food and foodstuffs in the economic regions, using the respective weight coefficients.
2. Main disaggregation
- Food/Foodstuffs;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Consumer price survey;
- Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 3. Ensuring healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
3.1.1. Maternal mortality ratio per 100,000 live births
1. Definition, calculation method
- Maternal mortality refers to the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of the termination of pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or childbirth, excluding deaths due to accidents or suicide.
- The maternal mortality ratio per 100,000 live births is the number of maternal mortalities in a region during the study period per 100,000 live births in the same region during the same period.
Formula:
![]()
In which:
MRb : Maternal mortality ratio per 100,000 live births;
![]() : Number of women who died due to causes related to pregnancy and childbirth during the study period;
: Number of women who died due to causes related to pregnancy and childbirth during the study period;
B: Number of live births in the study period.
2. Main disaggregation Ethnicity group (Kinh/other).
3. Publication frequency Every 10 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Health sector database (verified maternal death cases).
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Health.
3.1.2. Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel is the number of women giving birth during the reporting period who were assisted by skilled health personnel, calculated per 100 live births in the same period.
Skilled health personnel include obstetricians with at least a specialist orientation, midwives with intermediate or higher qualifications, pediatric and obstetric physicians, and other medical personnel authorized to practice in obstetrics and gynecology under the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment.
Formula:
|
Proportion of births attended by skilled health personnel (%) |
= |
Number of births attended by skilled health personnel in the reporting period |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of women giving birth in the reporting period |
2. Main disaggregation
- Ethnicity (Kinh/other);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in health sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
3.2.1. Under-five mortality rate
1. Definition, calculation method
The under-5 mortality rate measures the mortality level of children within their first five years of life. It is defined as the number of deaths of children under five years of age per 1,000 live births during the study period.
Formula:
In which:
U5MR: Under-five mortality rate;
5D0: Number of deaths of children under five years of age during the study period;
B: Number of live births in the study period.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
Ethnic disaggregation is published every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Socio-economic survey of 53 ethnic minorities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.2.2.a. Infant mortality rate
1. Definition, calculation method
The infant mortality rate measures the mortality level of children within their first year of life. It is defined as the number of deaths of children under one year of age per 1,000 live births during the study period.
Formula:
![]()
In which:
IMR : Infant mortality rate;
D0 : Number of deaths of children under one year of age during the study period ;
B : Number of live births in the study period.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
Ethnic disaggregation is published every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Socio-economic survey of 53 ethnic minorities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.3.1.a. Number of HIV infections detected per 100,000 population
1. Definition, calculation method
Number of HIV infections detected per 100,000 population represents the ratio of the total number of people diagnosed with HIV at the reporting time to the total population.
Formula:
|
Number of HIV infections detected per 100,000 population |
= |
Total number of people diagnosed with HIV at the reporting time |
˟ |
100,000 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in health sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Health.
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.3.2. Number of new tuberculosis (TB) cases per 100,000 population
1. Definition, calculation method
Number of new tuberculosis (TB) cases per 100,000 population refers to the number of newly diagnosed tuberculosis cases (all forms of tuberculosis) per 100,000 people in the given year.
Formula:
|
Number of new tuberculosis (TB) cases per 100,000 population |
= |
Total number of newly diagnosed tuberculosis patients in the given year |
˟ |
100,000 |
|
Average population in the same year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in health sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Health;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.3.3. Number of new malaria cases per 100,000 population
1. Definition, calculation method
Number of new malaria cases per 100,000 population refers to the number of newly detected malaria cases per 100,000 people in the given year.
Formula:
|
Number of new malaria cases per 100,000 population |
= |
Total number of newly detected malaria cases in the given year |
˟ |
100,000 |
|
Average population in the same year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in health sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Health;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.5.2. Percentage of people aged 15 and older consuming alcohol at a harmful level
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of people aged 15 and older consuming alcohol at a harmful level is the percentage of individuals aged 15 and older who consume alcohol at harmful levels relative to the total population aged 15 and older in the given year.
- Risk levels:
+ Low risk: Consumption ≤ 2 alcohol units/day for males, ≤ 1 alcohol unit/day for females, and not exceeding five days per week;
+ High risk: Consumption of 2 - ≤ 5 alcohol units/day;
+ Harmful level: Consumption ≥ 6 alcohol units/day or having consumed ≥ 6 alcohol units at least once in the past 30 days.
Formula:
|
Percentage of people aged 15 and older consuming alcohol at a harmful level |
= |
Number of people aged 15 and older consuming alcohol at a harmful level |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population aged 15 and older |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
3.6.1. Number of traffic accident; number of traffic injuries or deaths
1. Definition, calculation method
A traffic accident is an unexpected event occurring beyond human intent that takes place when traffic participants are operating on public roads, specialized roads, or public transportation areas (road networks including roads, railways, waterways, and airways). Such accidents result from subjective factors, violations of traffic safety regulations, or unforeseen incidents that could not be avoided in time, leading to damage to human life, health, or property.
A traffic accident case refers to a single or multiple consecutive collision involving traffic participants at a specific location. A traffic accident may involve one or multiple traffic participants.
The number of traffic accident victims includes individuals who are injured or deceased due to traffic accidents.
Traffic accident deaths refer to the total number of individuals who died as a result of traffic accidents.
Injured persons are individuals who have suffered physical or psychological harm due to the direct impact of a traffic accident, affecting their normal daily life.
The number of injured persons due to traffic accidents includes all individuals who required medical treatment as a result of traffic accidents.
2. Main disaggregation
- Type of accident (road/rail/waterway/maritime);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime in the public security sector;
- Statistical reporting regime in the transport sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge:
+ The Ministry of Public Security: Shall collect data on traffic accidents, deaths, and injuries from road, rail, and waterway transport;
+ The Ministry of Transport (the Vietnam Maritime Administration): Shall collect data on traffic accidents, deaths, and injuries from maritime transport.
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.7.1. The proportion of women aged 15-49 years with the need for family planning using modern contraceptive methods
1. Definition, calculation method
Modern contraceptive methods include female sterilization, intrauterine devices (IUDs), contraceptive implants, injectables, oral contraceptive pills, female condoms, barrier methods (including diaphragms, cervical caps, and spermicides in foam, gel, cream, or sponge form), lactational amenorrhea method (LAM), emergency contraception, and other modern methods such as contraceptive patches or vaginal rings.
The percentage of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning using modern contraceptive methods is the percentage of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning who are currently using (or whose spouse/partner is using) at least one modern contraceptive method, relative to the total number of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning.
Formula:
|
Percentage of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning using modern contraceptive methods (%) |
= |
Number of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning who are currently using (or whose spouse/partner is using) at least one modern contraceptive method |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of women aged 15-49 with the need for family planning |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Marital status;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Population and family planning change survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.7.2. Adolescent birth rate (10 -14 years; 15 -19 years)
1. Definition, calculation method
The adolescent birth rate (ages 10-14; 15-19) is defined as the total number of live births to adolescent mothers (ages 10-14; 15-19) per 1,000 women in the same age group.
Formula:
|
Adolescent birth rate (10 -14 years; 15 -19 years) |
= |
Total number of live births to adolescent mothers (ages 10-14; 15-19) |
˟ |
1000 |
|
Total number of adolescent women (ages 10-14; 15-19) |
2. Main disaggregation
- Mother's educational attainment;
- Age group (10-14; 15-19);
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency
- The birth rate for the 15-19 age group is published annually.
- The birth rate for the 10-14 age group is published every five years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Health.
3.8.1. Coverage of essential health services
1. Definition, calculation method
Coverage of essential health services is based on health interventions, including reproductive, maternal, neonatal, and child health services, population services, infectious and non-communicable disease management, service capacity, and accessibility, among the general population and the most disadvantaged groups.
This index is measured on a scale from 0 to 100, calculated as a weighted average of 14 health service coverage indexes:
- Percentage of women of reproductive age (15-49) who use and are satisfied with modern contraceptive methods.
- Percentage of pregnant women receiving at least four antenatal care visits.
- Percentage of children under 1 year old fully vaccinated
- Percentage of children under five years old suspected of pneumonia (with cough and difficulty breathing not due to congenital abnormalities or nasal blockage) in the two weeks before the survey who received treatment at a health facility.
- Tuberculosis detection and treatment success rate.
- Percentage of people infected with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- Percentage of the population in malaria-endemic areas who slept under an insecticide-treated bed net the night before the survey.
- Percentage of households with access to improved sanitation facilities.
- Percentage of adults aged 18 and older with normal blood pressure levels (according to age-standardized norms), regardless of treatment status.
- Percentage of adults aged 25 and older with normal blood glucose levels according to age-standardized norms.
- Percentage of the population aged 15 and older who use tobacco and have access to smoking cessation services.
- Number of hospital beds per capita, with a maximum threshold of 18 per 10,000 population.
- Number of health personnel (physicians, nurses, and pharmacists) per 10,000 population.
- International Health Regulations (IHR) core capacity index, which measures the percentage of 13 core capacities achieved at a specific time.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
3.8.2. Percentage of people living in households with large out-of-pocket health expenditures
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of people living in households with large out-of-pocket health expenditures is the percentage of individuals living in households where health expenditures exceed a significant proportion (more than 10% or 25%) of total household expenditures.
Formula:
|
Percentage of people living in households with large out-of-pocket health expenditures (%)
|
= |
Number of people living in households where health expenditures exceed 10% or 25% of total household expenditures |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of people living in surveyed households |
2. Main disaggregation
- Ethnicity of the head of the household;
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.a.1. Prevalence of current tobacco use among persons aged 15 years and older
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of people aged 15 and older using tobacco is the proportion of individuals aged 15 and older who currently use any tobacco product.
Tobacco products include products made wholly or partly from tobacco leaves, processed into cigarettes, cigars, loose tobacco for pipe smoking, and other forms of products used for smoking, chewing, or inhaling.
Formula:
|
Percentage of people aged 15 and older using tobacco (%) |
= |
Number of people aged 15 and older using tobacco |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population aged 15 and older |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Health;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
3.b.1. Percentage of children under 1 year old fully vaccinated
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of children under one year old fully immunized is the proportion of children under one year old who have received all vaccines required by the Ministry of Health, relative to the total number of children under one year old during the reporting period.
Formula:
|
Percentage of children under 1 year old fully vaccinated (%) |
= |
Number of children under one year old who have received all vaccines required by the Ministry of Health in the reporting period |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of children under one year old in the same reporting period |
2. Main disaggregation
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Regular reports from health facilities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Health.
3.c.1. Number of health workers per 10,000 people
1. Definition, calculation method
Health workers are individuals employed in health facilities (both public and private, including contract and permanent staff) at the reporting time in a given area.
Health workers include physicians, pharmacists, nurses, midwives, and other health personnel.
Formula:
|
Number of health workers per 10,000 population |
= |
Total number of health workers employed in health facilities at the reporting time |
˟ |
10,000 |
|
Total population |
2. Disaggregation
- Type of health worker (physician, pharmacist, nurse, midwife, other health personnel);
- Type of facility (public/private)
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Regular reports from health facilities;
- Health facility surveys.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Health;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 4. Ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
4.1.1. General school enrollment rate
1. Definition, calculation method
The general school enrollment rate consists of the overall enrollment rate and the age-appropriate enrollment rate for each level of education.
a) Overall enrollment rate:
The overall enrollment rate for primary education is the percentage of students enrolled in primary school relative to the total population aged 6-10.
The overall enrollment rate for lower secondary education is the percentage of students enrolled in lower secondary school relative to the total population aged 11-14.
The overall enrollment rate for upper secondary education is the percentage of students enrolled in upper secondary school relative to the total population aged 15-17.
Formula:
|
Overall enrollment rate at level i in academic year t (%) |
= |
Number of students enrolled at level i in academic year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Population in the age group for level i in academic year t |
b) Age-appropriate enrollment rate
The age-appropriate enrollment rate for primary education is the percentage of students aged 6-10 enrolled in primary school relative to the total population aged 6-10.
The age-appropriate enrollment rate for lower secondary education is the percentage of students aged 11-14 enrolled in lower secondary school relative to the total population aged 11-14.
The age-appropriate enrollment rate for upper secondary education is the percentage of students aged 15-17 enrolled in upper secondary school relative to the total population aged 15-17.
Formula:
|
Age-appropriate enrollment rate at level i in academic year t (%) |
= |
Number of students of school age level i studying at school level i in school year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Population in the age group for level i in academic year t |
The conventional student age is equal to the year of school commencement minus the student's year of birth on the birth certificate.
2. Main disaggregation
- General/age-appropriate enrollment;
- Education level (primary, lower secondary, upper secondary);
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime in the education sector;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Education and Training;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
4.1.2. Percentage of students completing primary, lower and upper secondary school
1. Definition, calculation method
a. The primary education completion rate is the percentage of students completing the primary education program in academic year t relative to the number of first-grade students in academic year (t-4).
Formula:
|
Primary education completion rate (%) |
= |
Number of students completing primary education in academic year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of first-grade students in academic year (t-4) |
b. The lower secondary education completion rate: is the percentage of students graduating from lower secondary school in academic year t relative to the number of sixth-grade students in academic year (t-3).
Formula:
|
Lower secondary education completion rate (%) |
= |
Number of students graduating from lower secondary school in academic year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of sixth-grade students in academic year (t-3) |
c. The upper secondary education completion rate is the percentage of students recognized as upper secondary school graduates in academic year t relative to the number of tenth-grade students in academic year (t-2).
Formula:
|
Upper secondary education completion rate (%) |
= |
Number of students recognized as upper secondary school graduates in academic year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of tenth-grade students in academic year (t-2) |
2. Main disaggregation
- Education level;
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Disability status;
- School type;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Education and Training.
4.2.2. Rate of mobilizing 5-year-old children to attend preschools
1. Definition, calculation method
The rate of mobilizing 5-year-old children to attend preschools is the percentage of 5-year-old children attending preschools, kindergartens, independent kindergarten classes, or other educational institutions relative to the total population of 5-year-old children.
Formula:
|
The rate of mobilizing 5-year-old children to attend preschools for academic year t (%) |
= |
Number of 5-year-old children enrolled in preschool, kindergarten in academic year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population of 5-year-old children in year t |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Education and Training.
4.3.1.a. Number of university students per 10,000 people
1. Definition, calculation method
The number of university students per 10,000 population is the ratio of students enrolled in undergraduate programs to every 10,000 people.
Formula:
|
Number of university students per 10,000 population |
= |
Number of students enrolled in undergraduate programs |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation School type.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Education and Training;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
4.3.1.b. Rate of trained workers
1. Definition, calculation method
The trained workforce includes:
- Workers with certificates/degrees: Mean individuals aged 15 and older who are employed or unemployed and have completed a formal vocational or technical training program within the national education system, holding one of the following qualifications: Certificate of elementary, intermediate, college, university, master's, doctorate, doctor of science.
- People who have not attended any technical training program but have acquired skills and expertise equivalent to level 1 of a technical worker with a degree/certificate in the same profession through self-study, training, or on-the-job training, and have actually done this job for 3 years or more. This group is commonly referred to as skilled workers without certificates/degrees.
Formula:
|
Percentage of trained workforce with certificates/degrees (%) |
= |
Number of trained workers with certificates/degrees |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total labor force |
|
Percentage of trained workforce (%) |
= |
Number of trained workers |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total labor force |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Technical and professional qualifications;
- Economic sector;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources:
- Labor and employment survey;
- Statistical reporting regime of the labor, invalids, and social affairs sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office): shall be in charge of collecting and synthesizing “the percentage of trained workforce with certificates/degrees (%)”.
- The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs shall shall be in charge of collecting and synthesizing “the percentage of trained workforce”.
4.4.1. The proportion of individuals aged 15–64 with information and communication technology (ICT) skills
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of people aged 15-64 with ICT skills represents the proportion of individuals aged 15-64 who possess ICT skills relative to the total population aged 15-64 in the reporting period.
Formula:
|
Percentage of people aged 15-64 with ICT skills (%) |
= |
Number of people aged 15-64 with ICT skills |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population aged 15-64 |
Criteria for determining ICT skills, as well as classification into basic and advanced skill levels, are established by the Ministry of Information and Communications to meet management requirements in each period and ensure international comparability.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Skill level (basic/advanced);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Information and Communications
4.5.1. Gender equality index in education across primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels
1. Definition, calculation method
The gender equality index in education at primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels is the ratio of a specific educational indicator for female students compared to male students. The closer the index is to 1, the higher the gender equality; the closer it is to 0, the greater the gender disparity.
Formula:
|
Gender equality index for indicator i |
= |
Value of indicator i for female students |
˟ |
100 |
|
Value of indicator i for male students |
In which:
i: The gross/net enrollment rate at primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels
2. Main disaggregation Education level.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime in the education sector;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Education and Training;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
4.6.1. The literacy rate of the population aged 15 and above
1. Definition, calculation method
The literacy rate of the population aged 15 and older is the percentage of individuals aged 15 and above who, at the time t, can read, write, and understand a simple sentence in the national language, ethnic language, or a foreign language, out of the total population aged 15 and older, at that time.
Formula:
|
The literacy rate of the population aged 15 and above (%) |
= |
Population aged 15 and older who are literate |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population aged 15 and older |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Ethnicity group (Kinh/other);
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Population and family planning change survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
4.7.1. The proportion of schools providing education on gender, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV awareness
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of schools providing education on gender, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV awareness is the proportion of schools that incorporate gender awareness, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV education into their curriculum, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at that educational level.
Formula:
|
Percentage of schools providing education on gender, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV awareness at level n (%) |
= |
Number of schools providing knowledge about gender, violence prevention, abuse prevention, and HIV awareness at level n |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of schools at level n |
2. Main disaggregation
- Education level;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Education and Training.
4.a.1. Percentage of schools with: (a) electricity; (b) Internet for learning purposes; (c) computers for learning purposes; (d) infrastructure and materials suitable for students with disabilities; (e) drinking water; (f) adequate and gender-specific sanitation facilities; and (g) convenient handwashing facilities
1. Definition, calculation method
This indicator represents the percentage of schools at each education level that have essential infrastructure or services available, including:
- Electricity Regular and available energy sources enable full and sustainable use of information and communication technology infrastructure for teaching and learning purposes.
- Internet for learning purposes: Internet access available for enhancing teaching and learning, accessible to students via fixed broadband, mobile broadband, or other means.
- Computers for learning purposes: Computers used to support course delivery or independent teaching and learning needs; including:
+ Desktops;
+ Laptops;
+ Tablets.
- Infrastructure suitable for students with disabilities: Facilities that allow unrestricted access for all users, including persons with disabilities. Accessibility includes ease of entry, exit, and use of school services.
- Accessible learning materials for students with disabilities include learning materials and assistive products enabling students with disabilities/functional limitations to access learning and participate fully in school. These may include textbooks, teaching materials, assessment tools, and other materials available and provided in appropriate formats such as audio, braille, sign language, and simplified formats that can be used by students with disabilities/functional limitations.
- Drinking water means water supply meeting the standards specified in Clause 1 Article 5 of Joint Circular No. 13/2016/TTLT-BYT-BGDDT dated May 12, 2016, of the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Education and Training, on regulations on healthcare activities in schools.
- Adequate gender-specific sanitation facilities: mean schools’ separate toilets for male and female students.
- Convenient handwashing facilities: Mean usable handwashing facilities with clean water and soap available to all male and female students.
Formula:
|
Percentage of schools at level n with facility f (%) |
= |
Number of schools at level n with facility f |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of schools at level n |
2. Main disaggregation
- Education level;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Education and Training.
4.c.1. The proportion of teachers meeting or exceeding the standard training level
1. Definition, calculation method
The percentage of teachers meeting or exceeding the standard training level is the proportion of teachers who have attained the prescribed qualification level or higher according to the education level (at the primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels), relative to the total number of teachers at the corresponding level.
Teachers who meet the required training standards at the primary, lower secondary, and upper secondary levels are teachers with a bachelor's degree in pedagogy, a bachelor's degree in teacher training or higher, or a bachelor's degree in a relevant major or higher and a certificate of pedagogical training.
Formula:
|
The proportion of teachers meeting or exceeding the standard training level (%) |
= |
Number of teachers meeting standards trained at level n in school year t |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total of teachers at school level n in school year t |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Education level;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the education sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Education and Training.
Goal 5. Achieving gender equality and empower all women and girls
5.1.1.a. Sex ratio at birth
1. Definition, calculation method
The sex ratio at birth is the number of male live births per 100 female live births in a given area during the reporting period (usually one year).
Formula:
|
Sex ratio at birth |
= |
Total number of male live births during the reporting period |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of female live births during the reporting period |
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Population and family planning change survey;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Health.
5.2.1. The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to physical violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months represents the percentage of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced physical, sexual, or emotional violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the past 12 months compared to the total number of women and girls aged 15 years and over.
Types of violence include:
a) Physical violence, including acts intended to harm the victim, such as pushing, grabbing, twisting arms, pulling hair, slapping, kicking, biting, punching, or threatening or attacking with weapons, guns, or knives, etc.
Formula:
|
Percentage of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced physical violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months (%) |
= |
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced physical violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the past 12 months |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of women and girls aged 15 and older |
b) Sexual violence means unwanted or harmful sexual acts imposed on a person, including acts of sexual abuse, forced sexual contact, attempted or completed sexual acts without consent, incest, sexual harassment, etc.
Formula:
|
Percentage of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced sexual violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months (%) |
= |
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced sexual violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older |
c) Emotional violence means acts of emotional abuse and controlling behavior, often associated with physical and sexual violence by a spouse or intimate partner.
|
Percentage of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced emotional violence by a current or former spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months (%) |
= |
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced emotional violence by a spouse or intimate partner in the previous 12 months |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Ethnicity;
- Educational attainment;
- Type of violence (physical/sexual/emotional);
- Frequency of violence;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.2.2. The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the previous 12 months
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the previous 12 months represents the percentage of women and girls aged 15 and older who have experienced sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the past 12 months compared to the total number of women and girls aged 15 and older.
Formula:
|
The proportion of women and girls aged 15 years and over subjected to sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the previous 12 months (%) |
= |
Number of women and girls aged 15 years and over who have ever been subjected to sexual violence by a person other than their husbands or intimate partners in the previous 12 months |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of women and girls aged 15 and older |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Location of incident;
- Educational attainment;
- Ethnicity;
- Frequency of violence;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.3.1. The proportion of women aged 20 - 24 who were first married or in union before age 15 or 18
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women aged 20 - 24 who were first married or in union before age 15 or 18 represents the percentage of women aged 20-24 who were first married or in union before the ages of 15 and 18, relative to the total number of women aged 20-24.
Formula:
|
Percentage of women aged 20-24 who were first married or in union before age 15 or 18 (%) |
= |
Number of women aged 20 - 24 who were first married or in union before age 15 or 18 |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of women aged 20-24 |
2. Main disaggregation
- Ethnicity (Kinh/other);
- Educational attainment;
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.3.1.a. The proportion of child marriages
1. Definition, calculation method
Child marriage refers to the act of getting married when one or both individuals have not reached the legally prescribed age for marriage.
According to the Law on Marriage and Family, the legal minimum marriage age is 20 years for males and 18 years for females.
The child marriage rate is the percentage of cases where individuals marry or cohabit as spouses before reaching the legal age, relative to the total number of married or cohabiting cases.
2. Main disaggregation Ethnicity.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Mid-term population and housing survey;
- Socio-economic survey of 53 ethnic minority groups.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency in charge: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Committee for Ethnic Minority Affairs.
5.4.1. The proportion of time spent on unpaid domestic and care work
1. Definition, calculation method
Unpaid domestic and care work includes activities such as meal preparation, dishwashing, house cleaning and repairs, laundry, gardening, pet care, shopping, assembling, maintaining, and repairing personal and household items, childcare, and care for the sick, elderly, or disabled family members, etc.
Formula:
|
Proportion of time spent on unpaid domestic and care work (%) |
= |
Average daily hours spent on unpaid domestic and care work |
˟ |
100 |
|
24 |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.5.1.a. The proportion of women in the National Assembly
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women in the National Assembly is the percentage of female representatives relative to the total number of National Assembly members within the same term.
Formula:
|
The proportion of women in the National Assembly for term k (%) |
= |
Number of female National Assembly representatives in term k |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of National Assembly representatives in term k |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Educational attainment;
- Ethnicity.
3. Publication frequency: At the beginning of each term.
4. Data sources: Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The National Assembly Office.
5.5.1.b. The proportion of women in People's Councils
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women in the provincial-level People's Council (province or centrally run city) is the percentage between the number of female delegates to the People's Council at the provincial level compared to the total number of delegates to the provincial-level People's Council in the same term.
The proportion of women in the district-level People's Council (rural district, district, town, provincial city, or city under centrally run city) is the percentage between the number of female delegates to the People's Council at the district level compared to the total number of delegates to the district-level People's Council in the same term.
The proportion of women in commune-level People's Council (commune, ward or town) is the percentage between the number of female delegates to the People's Council at the commune level compared to the total number of delegates to the commune-level People's Council in the same term.
Formula:
|
Proportion of women in the People’s Council at level t for term k (%) |
= |
Number of female delegates in the People’s Council at level t for term k |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of delegates in the People’s Council at level t for term k |
2. Main disaggregation
- Administrative level;
- Ethnicity;
- Age group;
- Educational attainment.
3. Publication frequency At the beginning of each term.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in home affairs sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Home Affairs.
5.5.2. The proportion of women in leadership positions across sectors, levels, and units
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of women in leadership positions across sectors, levels, and units measures the percentage of female workers holding leadership roles across different sectors, levels, and units, compared to the total number of workers who are leaders in sectors, levels and units.
Leadership positions in sectors, levels, and units are classified based on the Vietnam Standard Occupational Classification (VSOC) issued by the Prime Minister.
Formula:
|
Proportion of women in leadership positions across sectors, levels, and units (%) |
= |
Number of female leaders across sectors, levels and units |
˟ |
100 |
|
Number of leaders across sectors, levels and units |
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.6.1. The proportion of women aged 15 - 49 who make their own decisions on sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care
1. Concepts, calculation methods
The proportion of women aged 15 - 49 who make their own decisions on sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care reflects the percentage of women aged 15-49 who may select or make their own decision on all three areas such as sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care.
Formula:
|
The proportion of women aged 15 - 49 who make their own decisions on sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care (%) |
= |
The number of women aged 15 - 49 who may select or make their own decisions on sexual relations, contraceptive use, and reproductive health care |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of women aged 15-49 |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Educational attainment;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Population and family planning change survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.a.1. The proportion of agricultural land-using households with land use certificates
1. Definition, calculation method
An agricultural land-using household is a household that has engaged in cultivation activities over the past 12 months on agricultural land, including long-term allocated land, transferred land, leased land, borrowed land, or tendered land;
excluding: Households engaged in forestry, fishing, and aquaculture activities; households owning agricultural land but not cultivating it; households with members working in agriculture only as wage laborers.
The proportion of agricultural land-using households with land use certificates is the percentage of such households that possess land use rights certificates for such agricultural land areas, compared to the total number of agricultural land-using households.
Formula:
|
Proportion of agricultural land-using households with land use certificates (%) |
= |
Number of agricultural land-using households with land use certificates |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total number of agricultural land-using households |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender of household head;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Rural, agricultural and fishery census;
- Mid-term rural and agricultural survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
5.b.1. The proportion of individuals owning mobile phones
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of individuals owning a mobile phone is the percentage of individuals who own a mobile phone relative to the total population in the reporting period.
Formula:
|
Proportion of individuals owning mobile phones (%) |
= |
Number of individuals owning mobile phones |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population |
Depending on the management requirements of each period and to ensure the goal of international comparison, the number of individuals owning mobile phones is regulated according to a certain age. Therefore, the scope of data collection will be specifically regulated in each survey plan.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Ethnicity;
- Disability status;
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
Disaggregation by disability status is published every five years.
4. Data sources
- Vietnam household living standards survey;
- National disability survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 6. Ensuring sufficient water and latrine systems, sustainable management of water resources
6.1.1. The proportion of population using safely managed drinking water sources
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of the population using safely managed drinking water sources is the percentage of the population using clean water sources compared to the total population.
Formula:
|
The proportion of population using safely managed drinking water sources (%) |
= |
Number of populations using safely managed drinking water sources |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population |
Safely managed drinking water sources are the main sources of water used for eating and drinking in households as follows:
- Piped supplies;
- Boreholes and tube wells;
- Protected dug wells;
- Protected springs;
- Rainwater;
- Water purchased from tanker trucks;
- Bottled water.
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
6.2.1. The proportion of population using safely managed sanitation facilities
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of the population using safely managed sanitation facilities is the percentage of individuals using an improved sanitation facility relative to the total population.
Formula:
|
Proportion of population using safely managed sanitation facilities (%) |
= |
Population using safely managed sanitation facilities |
˟ |
100 |
|
Total population |
Safely managed sanitation facilities include:
- Septic tanks, flush toilets;
- Improved pit latrines with ventilation pipes or covered seats;
- Composting toilets.
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Provinces, centrally-run cities;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
6.3.1. The proportion of urban wastewater collected and treated according to standards and regulations
1. Definition, calculation method
- Wastewater refers to used water that is discharged into the environment. Wastewater treatment involves using technological and technical solutions to reduce, remove, or eliminate harmful components, ensuring treated wastewater discharged into the environment meets prescribed standards and regulations.
- The proportion of urban wastewater collected and treated according to standards and regulations is the percentage of urban wastewater that is collected and treated to meet prescribed standards and regulations relative to 80% of the total clean water supply capacity in the locality.
Formula:
|
The proportion of urban wastewater collected and treated according to standards and regulations (%) |
= |
Total urban wastewater treatment capacity |
x 100 |
|
Total water supply of the water plant x 80% |
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban classification (Special cities/Type I/Type II/Type III/Type IV/Type V);
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the construction sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Construction.
6.3.1.a. The proportion of operating industrial zones with centralized wastewater treatment systems meeting environmental standards
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of operating industrial zones with centralized wastewater treatment systems meeting environmental standards indicator represents the percentage of operational industrial zones equipped with centralized wastewater treatment plants that meet environmental standards, out of the total number of operational industrial zones.
Formula:
|
Proportion of operating industrial zones with centralized wastewater treatment systems meeting environmental standards (%) |
= |
Number of industrial zones with centralized wastewater treatment plants meeting environmental standards |
x 100 |
|
Total number of operational industrial zones |
2. Main disaggregation Provinces and centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime in the planning and investment sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the Department for Economic Zones Management)
6.4.1. a. The proportion of large reservoirs monitored and controlled to ensure the maintenance of minimum river basin flows
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of large reservoirs monitored and controlled to ensure minimum river basin flow represents the percentage of large reservoirs subject to monitoring and control to maintain minimum river flow relative to the total number of large reservoirs.
Monitoring and control are carried out in accordance with regulations issued by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Minimum river flow refers to the lowest flow required to sustain a river or a river segment, ensuring the normal development of aquatic ecosystems and maintaining a minimum level of water exploitation and use activities for water users.
Formula:
|
Proportion of large reservoirs monitored and controlled for minimum river basin flow (%) |
= |
Number of large reservoirs monitored and controlled for minimum river basin flow |
x 100 |
|
Total number of large reservoirs |
2. Publication frequency Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
6.4.1.b. The proportion of large and important reservoirs in river basins operated according to inter-reservoir coordination regulations
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of large and important reservoirs in river basins operated according to inter-reservoir coordination regulations represents the percentage of large, important reservoirs in river basins operated under inter-reservoir coordination regulations compared to the total number of large, important reservoirs in river basins.
The large and important reservoirs in river basins operated under the inter-reservoir coordination regulations include those listed in the Prime Minister’s List of irrigation and hydropower reservoirs in river basins.
Formula:
|
The proportion of large and important reservoirs in river basins operated according to inter-reservoir coordination regulations (%) |
= |
Number of large and important reservoirs in river basins operated according to inter-reservoir coordination regulations |
x 100 |
|
Total number of large, important reservoirs in river basins |
2. Publication frequency Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
6.6.1.a. The number of Ramsar sites established and recognized
1. Definition, calculation method
A Ramsar Site is a wetland of international importance recognized by the Ramsar Convention Secretariat. According to the above regulation, the Ramsar Convention is the abbreviation of the Convention on Wetlands of International Importance.
2. Publication frequency Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Goal 7. Ensuring access to sustainable, reliable and affordable energy for everyone
7.1.1. The proportion of the population with access to electricity
1. Definition, calculation method
The proportion of the population with access to electricity refers to the percentage of the population using electricity over the total population (only the population using grid electricity is counted).
Formula:
|
Proportion of the population with access to electricity (%) |
= |
Population using electricity |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region.
- Provinces, centrally-run cities.
3. Publication frequency Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
7.1.2. The proportion of households using clean fuels
1. Definition and calculation method
Clean fuel refers to a type of fuel that has minimal environmental impact during its production, utilization, and disposal. The main characteristics of a clean fuel include:
+ Low emissions: generation of minimal harmful emissions such as CO₂, NOₓ, SOₓ, and fine particulate matter during combustion.
+ Renewability: It can be regenerated or sourced from inexhaustible resources.
+ Environmental friendliness: Causing of minimal negative impacts on ecosystems and human health.
+ High energy efficiency: Ability to effectively convert energy.
A number of examples of clean fuels include:
+ Electricity: Especially electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydro power.
+ Hydrogen: When it is produced from water by use of renewable energy for water splitting.
+ Biogas: Produced from the biological decomposition of organic materials.
+ Biofuels: Such as ethanol and biodiesel, derived from plants or biological waste.
+ Natural gas: Although the natural gas is not entirely emissions-free, it is considered as a relatively cleaner energy source than coal and oil.
Households using clean fuels for cooking mean those primarily using electric stoves, solar cookers, LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), gas/biogas stoves, or ethanol/alcohol-based stoves.
Households using clean fuels for heating mean those mainly using central heating systems, or solar or electric heaters, heaters using natural gas pipeline, LPG/liquefied gas, biogas, or ethanol/alcohol.
Households using clean fuels for lighting mean those primarily using electricity, solar lamps, rechargeable or battery-operated lamps, or natural gas-powered lamps.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of households using clean fuels (%) |
= |
The number of households primarily using clean fuels for cooking, heating and lighting |
x 100 |
|
|
Total households |
|
|||
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender of the head of the household;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
7.2.1. Share of renewable energy in total final energy consumption
1. Definition and calculation method
Renewable energy consumption includes energy consumption from the following sources: Hydropower, solid biofuels, wind, solar, liquid biofuels, biogas, geothermal, ocean waves, and waste. The total final energy consumption derived form the national statistical data and energy balance means the total final consumption excluding non-energy use.
Specific Renewable Energy Sources:
- Solar energy;
- Hydropower;
- Wind energy;
- Liquid biofuels, including bioethanol, biodiesel, and other liquid biofuels;
- Solid biofuels, including firewood, animal waste, plant waste, black liquor, bagasse, and charcoal, etc.;
- Energy from waste, including energy derived from renewable urban waste.
Final energy consumption refers to the energy directly consumed by society, where energy is completely utilized without generating new energy sources. Energy used in the final consumption does not include energy used in the processing of new energy types.
Calculation formula:
|
The share of renewable energy in total final energy consumption (%) |
= |
Renewable energy |
x 100 |
|
Total final energy consumption |
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3 Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The General Statistics Office;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Industry and Trade.
7.3.1.a. Total primary energy supply per GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
Total primary energy supply per GDP means the indicator reflecting the relationship between energy consumption and GDP. It measures how much units of energy are required to generate one unit of gross domestic product (GDP).
Primary energy refers to energy extracted or directly obtained from natural resources without undergoing conversion processes. It includes fossil fuels (such as coal, oil shale, peat and peat products, crude oil, and natural gas), biofuels, waste, nuclear energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, solar energy, wind energy, and heat from heat pumps sourced from the surrounding environment.
Total primary energy supply represents the total amount of energy a country utilizes over a specified period and is calculated as follows:
Calculation formula:
|
Total primary energy supply |
= |
Primary energy production |
+ |
Energy imports (including primary and converted energy) |
- |
Energy exports (including primary and converted energy) |
- |
International aviation and maritime reserves (including primary and converted energy) |
+ |
Stock change (including primary and converted energy) |
|
Total primary energy supply per GDP |
= |
Total primary energy supply |
|
GDP |
Total primary energy supply is measured in ton of oil equivalent (TOE), while GDP is calculated at constant prices.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data source
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Industry and Trade; the Ministry of Construction; the Ministry of Transport; the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
7.3.1.b. Energy intensity per gross domestic product (GDP)
1. Definition and calculation method
Energy consumption includes energy used for production and energy used for daily activities.
Energy used for production and daily activities consists of: Gasoline, oil, gas, coal, electricity, etc.
Calculation formula:
|
Energy intensity per gross domestic product (GDP)(%) |
= |
Energy intensity |
x 100 |
|
|
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
3. Announcement period: Year.
4. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Industry and Trade.
7.b.1. Installed capacity of renewable energy
1. Definition and calculation method
Renewable energy includes Electricity from solar energy, electricity from wind energy, electricity from tidal energy.
a. Installed capacity of solar power
Solar power output refers to the amount of electricity produced from solar energy, measured at the production meter at the generation site before being transferred to the consumer over a specified period.
Solar energy is the radiant light and heat from the sun that has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies.
Applications of solar energy include: Solar water heating, lighting, solar cooking, water distillation and sterilization, solar electricity, space heating and cooling through solar architecture, high-temperature thermal storage for industrial purposes, solar electricity based on thermal engines and photovoltaic cells.
Calculation method:
The most common method of solar energy collection is the use of solar panels. Solar energy technologies are classified into two main categories being active solar technologies and passive solar technologies, depending on the method of collection, conversion, and distribution of solar energy.
Active solar technologies involve the use of photovoltaic (PV) panels and solar thermal collectors. Such technologies that enhance the energy supply are referred to as supply-side technologies. Passive solar technologies include building orientation toward the sun, selection of materials with favorable thermal mass, light diffusion effects, and space design with natural ventilation. Passive solar technologies that reduce energy demand are referred to as demand-side technologies.
Within the scope of such indicator, only solar energy used for electricity production is considered or only electricity output generated from solar energy is accounted for.
Solar power capacity refers to the electricity production capability of a power plant based on its installed capacity. Thus, the used measurement units are consistent with units used for other power sources: Watt (W) and its multiples being Kilowatt (kW) and Megawatt (MW).
Electricity output is the amount of electricity produced over a specified period, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Electricity output is measured at the production meter before being transferred for consumption.
The electricity generated is recorded at the generator of each unit through the plant’s main meter, which separates the self-consumption electricity and transformer losses, the remaining is the consumed electricity.
b. Installed capacity of wind power
Installed capacity and wind power output refers to the amount of electricity produced from wind energy, measured at the production meter before being transferred to the consumer during a specified period.
Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air moving within the Earth's atmosphere. Wind energy is considered an indirect form of solar energy. The utilization of wind energy is among the earliest known methods of harnessing natural energy resources and has been recognized since ancient times.
Wind energy describes the process by which wind is harnessed to produce mechanical or electrical energy. Wind turbines convert the wind’s kinetic energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy may be utilized for specific tasks (such as grinding grain or pumping water), or a generator may convert such mechanical energy into electricity for a power plant.
Wind is a form of solar energy, resulting from the Sun’s uneven heating of the Earth's atmosphere, the earth's irregular surfaces, and the planet's revolution around the sun. Wind flow patterns are modified by the Earth’s terrain, bodies of water, and vegetation coverage. This energy wind flow or motion can be harnessed by modern wind turbines to generate electricity.
Calculation method
Within the scope of such indicator, only wind energy used for electricity production is considered or only electricity output generated from wind energy is accounted for.
Wind power capacity refers to the electricity production capability of a power plant, thus, the used measurement units are consistent with units used for other power sources: Watt (W) and its multiples being Kilowatt (kW) and Megawatt (MW).
Electricity output is the amount of electricity produced over a specified period, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Electricity output is measured at the production meter before being transferred for consumption.
The electricity generated is recorded at the generator of each unit through the plant’s main meter, which separates the self-consumption electricity and transformer losses, the remaining is the consumed electricity.
c. Installed capacity of tidal power
Installed capacity and tidal power output refers to the amount of electricity produced from tidal energy, measured at the production meter before being transferred to the consumer during a specified period.
The tidal power is harnessed by converting energy from the rise and fall of the tide every day. By harnessing tidal currents, systems of electricity generation equipment are installed.
Currently, there are two types of extraction technologies being applied in various countries around the world to effectively utilize this energy source: extraction technology based on the kinetic energy of tidal currents and extraction technology based on the potential energy of tides.
For the technology that relies on the potential energy of tides, it is necessary to construct a reservoir and utilize the tide to create a difference in the static water column between the mass of water within the reservoir and that of the sea, or vice versa. Water turbines are employed to generate electricity. The advantage of this technology is mitigating the instability of tidal energy; however, it encounters difficulties when dams must be constructed to form reservoirs in coastal areas, which often feature complex terrain conditions.
Currently, certain regions around the world have deployed power generation systems utilizing tidal energy.
Calculation method:
Tidal power capacity refers to the electricity production capability of a power plant, thus, the used measurement units are consistent with those used for other power sources: Watt (W) and its multiples being Kilowatt (KW) and Megawatt (MW).
Electricity output is the amount of electricity produced over a specified period, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Electricity output is measured at the production meter before being transferred for consumption.
The electricity generated is recorded at the generator of each unit through the plant’s main meter, which separates the self-consumption electricity and transformer losses, the remaining is the consumed electricity.
2. Main disaggregation
- Capacity;
- Type of energy (solar/wind/tidal energy).
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Survey on production capacity of selected industrial products.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Industry and Trade.
Goal 8. Promoting sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
8.1.1. The growth rate of GDP per capita
1. Definition and calculation method
The GDP per capita is calculated by dividing the GDP in a year by the average population in the corresponding year. The GDP per capita can be calculated at current prices, in domestic or foreign currency, or the growth rate of GDP per capita is calculated at constant prices.
Calculation formula:
|
GDP per capita |
= |
GDP in the year (VND) |
|
Average population in the year |
The GDP per capita in foreign currency is calculated in USD at the (current) exchange rate or purchasing power parity.
|
The GDP per capita in at the exchange rate or purchasing power parity (USD) |
= |
GDP per capita (VND) |
|
The average annual purchasing power parity exchange rate or exchange rate VND/USD |
The growth rate of GDP per capita is calculated according to the following formula:
|
The growth rate of GDP per capita (%) |
= |
GDP per capita of the reporting year |
x 100 -100 |
|
GDP per capita of the year preceding the reporting year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data;
- The exchange rate of the Vietnamese Dong (VND) to the US Dollar (USD) is announced by the Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office), based on the report of the State Bank of Vietnam; the purchasing power parity exchange rate is calculated by the Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office) based on data published by the World Bank.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.1.1.b. The growth rate of gross domestic product (GDP)
1. Definition and calculation method
a) Calculation of the growth rate of gross domestic product (GDP) for a given quarter, six-month period, nine-month period, or year
The growth rate of gross domestic product (GDP) for a given quarter, six-month period, nine-month period, or year is the percentage increase in the GDP of the current period compared to the GDP of the corresponding period of the immediately preceding year.
The growth rate of GDP shall be calculated at constant prices using the following formula:
|
The growth rate of GDP (%) |
= |
GDPn1 |
x 100 -100 |
|
GDPn0 |
In which:
GDPn1 : Refers to the GDP at constant prices for the reporting quarter, six-month period, nine-month period, or year;
GDPn0: Refers to the GDP at constant prices for the quarter, six-month period, nine-month period, or year preceding the reporting year.
b) Calculation of the growth rate of GDP by period (multiple years)
Calculation formula:
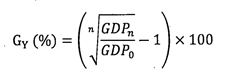
In which:
GY: The average annual GDP growth rate by period; from the year immediately following the base year to the nth year
GDPn: GDP at constant prices for the final year (the nth year) of the period of study;
GDP0: GDP at constant prices for the base year of the period of study;
n: The number of years counted from the year immediately following the base year up to the reporting year.
2. Main disaggregation
- Economic sector;
- Form of economic organization;
- Use purpose;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.2.1. The growth rate of labor productivity
1. Definition and calculation method
Labor productivity is an indicator reflecting the efficiency of the workforce, commonly measured by the gross domestic product per worker during the relevant reference period.
Calculation formula:
|
Labor productivity (VND/worker) |
= |
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
|
The average total of employed workers |
The growth rate of labor productivity is calculated using the following formula:
|
The growth rate of labor productivity (%) |
= |
Labor productivity of the reporting year |
x 100 -100 |
|
Labor productivity of the year preceding the reporting year |
2. Main disaggregation
- Economic sector (or region);
- Form of economic organization.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.3.1. The proportion of workers in informal employment
1. Definition and calculation method
Workers in informal employment consists of individuals whose work falls under one of the following five categories: (i) Unpaid family workers; (ii) Owners of establishments or self-employed persons operating in the informal sector; (iii) Wage earners who do not have a labor contract, or have a labor contract but are not covered by mandatory social insurance paid by their employer; (iv) Cooperative members who do not participate in mandatory social insurance; (v) Self-employed individuals or wage earners in households or in agricultural, forestry, and fishery households.
Workers in the agricultural, forestry and fishery households.
The proportion of workers in informal employment means the percentage of workers in informal employment to the total number of employed workers.
Calculation formula:
|
The proportion of workers in informal employment (%) |
= |
The number of workers in informal employment |
x 100 |
|
The number of employed workers |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Technical or professional qualifications;
- Economic sector;
- Economic zone;
- Form of economic organization;
- Occupation;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.5.1. The average income per employed worker
1. Definition and calculation method
The income of employed persons includes the following incomes:
- Income from wages, salaries, and other wage-like compensation, including overtime pay, bonuses, allowances, etc., for wage earners in the economy. These incomes may be in cash or in kind.
- Income from production and business activities, consisting of profits derived from agricultural production for sale, or profits from trading goods or services, etc. This does not include income from interest on loans or dividends unrelated to one’s current job.
The average income of an employed person is the total income of all such employed persons compared to the total number of employed persons.
Calculation formula:
|
The average income per employed worker |
= |
The total income of all employed workers |
|
The total number of employed workers |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Occupation;
- Economic sector;
- Urban/rural area;
- Socio-economic region;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.5.2. The unemployment rate
1. Definition and calculation method
An unemployed person is any individual aged 15 or older who, during the reference period, meets all three of the following conditions: he/she is not currently working, is actively seeking employment, and is available to work.
- Unemployed persons also include those who are not currently working and are available to work but did not seek employment during the reference period because they already had a definite job or business activity to begin after the reference period.
The unemployment rate means the percentage of the unemployed persons to the labor force.
Calculation formula:
|
The unemployment rate (%) |
= |
The number of unemployed persons |
x 100 |
|
The labor force |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Technical or professional qualifications;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.6.1. The proportion of youth aged 15 - 24 not in employment, education, or training (NEET)
1. Definition and calculation method
The proportion of youth aged 15 - 24 not in employment, education, or training means the percentage of youth aged 15 - 24 currently not in employment, education, or training to the total number of youth aged 15 - 24.
Calculation formula:
|
The proportion of youth aged 15 - 24 not in employment, education, or training (%) |
= |
The total number of youth aged 15 - 24 – The number of youth aged 15 - 24 in employment – The number of youth aged 15 - 24 currently not in employment, but enrolled in education or training |
x 100 |
|
The total number of youth aged 15 - 24 |
Or
|
The proportion of youth aged 15 - 24 not in employment, education, or training (%) |
= |
(The number of unemployed youth aged 15 - 24 + The number of youth aged 15 - 24 not in the labor force) – (The number of unemployed youth aged 15 - 24 currently enrolled in education or training + The number of youth aged 15 - 24 not in the labor force who are currently enrolled in education or training) |
x 100 |
|
The total number of youth aged 15 - 24 |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
8.7.1. The proportion of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor
1. Definition and calculation method
Children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor mean those aged full 5 - 17 who, during the reference period, worked for at least one hour to produce goods or provide services for the purpose of earning wages, salaries, or profits, or to assist a family member who receives wages or salaries. Such work excludes household chores within the family and/or chores at school or tasks of self-consumption family agriculture.
The proportion of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor is the percentage of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor to the total number of population aged 5 - 17.
Calculation formula:
|
The proportion of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor (%) |
= |
The number of children aged 5 - 17 engaged in child labor |
x 100 |
|
The total number of population aged 5 - 17 |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group (5 - 15, 16 - 17);
- Economic sector;
- Occupation;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
8.8.1. The number of work-related accidents
1. Definition and calculation method
Work-related accidents means an accident causing injury to any part or function of the body or causing death to employees, which happens during the working process and is closely related to the performance of the assigned work or task, also including those happens during the time of activities of breaks between working hours, mid-shift meals, in-kind meals, menstruation breaks, shower time, breastfeeding time, toilet use, preparation of and finish to work at the workplace.
Work-related accidents are classified as follows:
- Fatal work-related accidents;
- Serious work-related accidents (causing serious injuries);
- Minor work-related accidents (causing minor injuries).
The victim of the work-related accident means an individual who has been injured or has died in a work-related accident. A fatal work-related accident is an accident in which the victim dies immediately at the place where the accident occurs, or on the way to hospital; dies while being given emergency treatment; dies during treatment; or dies of recrudesce from injuries caused by the work-related accidents (according to the conclusion stated in a forensic medical examination record).
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Type of injury;
- Number of deaths;
- Economic sector;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting mechanism of the labor, invalids, and social affairs sector.
Statistical reports of Departments of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs of provinces and centrally-run cities under the Decree No. 39/2016/ND-CP dated May 15, 2016 of the Government, detailing a number of articles of the Law on Occupational Safety and Health.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs.
8.9.1. The contribution of tourism activities to GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
The contribution of tourism activities to GDP is calculated by the added value of tourism activities compared to GDP at current prices. The added value of tourism activities is generated by all sectors to satisfy the tourism consumption needs of both domestic and international tourists within the territory of Vietnam during their trips.
Domestic tourists are Vietnamese citizens, foreigners permanently residing in Vietnam who travel within the territory of Vietnam.
International tourists to Vietnam are those who are not permanent residents of Vietnam where they stay for less than one consecutive year, with the purpose of their visit not being to earn money.
The economic sub-sectors of tourism activities include accommodation, food and beverage, transportation, retail, and other services (such as healthcare, entertainment, insurance, etc.).
The disaggregation of the contribution of green tourism activities in GDP is calculated in a manner similar to the contribution of tourism activities in GDP. Based on the data on the added value of tourism activities categorized by the services of travel, accommodation, food and beverage, transportation, trade and others, combined with the indicators such as the proportion of green-labeled establishments and the percentage of vehicles operating on electricity or green energy compiled and reported by the authorities, the disaggregation of the added value of green tourism in tourism activities shall be calculated.
Calculation formula:
|
The contribution of tourism activities to GDP of the year (n) |
= |
The added value (VA) of tourism activities of the year (n) |
x 100 |
|
GDP at current prices of the year (n) |
2. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
3. Data sources
- Statistical survey (Tourist expenditure surveys, Household expenditure surveys that include expenditures on tourism activities, annual surveys of businesses and individual establishments providing travel services);
- Statistical report (Number of domestic tourists, number of international tourists of each year, the proportion of tourist attractions, shopping destinations, rest stops, restaurants serving tourists that have been granted green labels, the proportion of lodging establishments awarded the Green Lotus label), the proportion of vehicles using electricity or green energy, etc., serving the calculation of indicators related to tourism activities, as promulgated, labeled, and listed in statistical reports by competent agencies;
- Other sources: Intermediate cost coefficients and the most recently updated inter-sectoral balance sheets.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
8.10.1. The number of commercial bank branches and ATMs per 100,000 population aged 15 and above
1. Definition and calculation method
Branch of a commercial bank means a dependent unit of a commercial bank which applies dependent accounting, has a seal and is assigned to perform one or several functions of a commercial bank as decentralized by the commercial bank in accordance with law regulations.
ATM refers to an automated teller machine that clients can use to perform transactions such as depositing, loading, and withdrawing cash, transferring money, paying for goods and services, checking account balances, or carry out other transactions in accordance with law regulations.
Calculation formula:
|
The number of commercial bank branches per 100,000 population aged 15 and above |
= |
The number of bank branches |
x 100,000 |
|
The population aged 15 and above |
|
The number of ATMs per 100,000 population aged 15 and above |
= |
The number of ATMs |
x 100,000 |
|
The population aged 15 and above |
2. Main disaggregation Province, centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- The number of commercial bank branches and the number of ATMs: Administrative data;
- The population aged 15 and above: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The State Bank of Vietnam: Provide the data on the number of commercial bank branches and the number of ATMs;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office): Provide the data on the population aged 15 and above.
8.10.2. The proportion of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions
1. Definition and calculation method
The proportion of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions means the percentage of people aged 15 and above with an active transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions to the population aged 15 and above
Calculation formula:
|
The proportion of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions (%) |
= |
The number of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions |
x 100 |
|
The population aged 15 and above |
- The population aged 15 and above refer Vietnamese nationals who are 15 years of age or older.
- Accounts consist of: Payment accounts; bank cards opened or issued by credit institutions or foreign bank branches; Mobile Money accounts provided by authorized telecommunications businesses.
+ Payment account means a demand deposit account opened by a customer at a bank to use payment services provided by such bank.
+ Bank card is a payment instrument issued by a card issuer to perform card transactions under the conditions and terms agreed upon by the parties, excluding cards issued by organizations providing goods and services that are only used to pay for goods and services of those issuing organizations.
+ Mobile Money accounts refer telecommunications accounts to pay for small-value goods and services provided by telecommunications businesses to customers.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- The number of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized institutions: Administrative data;
- The population aged 15 and above: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The State Bank of Vietnam: Provide the data on the number of people aged 15 and above with a transaction account at banks or other authorized;
- Coordinating agency:
+ The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office): Provide the data on the population aged 15 and above.
+ The Ministry of Public Security.
Goal 9: Building highly resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and innovation
9.1.2.a. Number of passenger trips transported and transited
1. Definition and calculation method
a) Number of passenger trips transported
The number of passenger trips transported refers to the number of passengers transported by specialized transport entities and by units within other sectors that conduct transport business, regardless of the distance traveled. The number of passengers transported corresponds to the actual number of passengers who were transported.
b) Number of passenger trips transited
The number of passenger trips transited refers the number of transported passengers calculated by the length of the transport distance.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of passenger trips transited |
= |
Number of passenger trips transported |
x |
The transport distance |
In which:
The transport distance is the distance used for fare calculation, as prescribed by the competent agency.
For passenger vehicles rented under a per-trip transport contract, the number of passengers transported under each contract is only counted once according to the number of seats of the vehicle.
2. Main disaggregation
- Transport industry (railway/road/waterway/airway);
- Form of economic organization;
- Domestic/foreign country;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Economic census;
- Enterprise survey;
- Survey of individual production and business establishments;
- Survey of trade and service activities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.1.2.b. Volume of goods transported and transited
1. Definition and calculation method
a) Volume of goods transported
a) Volume of goods transported
The volume of goods transported is the mass of goods that have been transported during the period, regardless of the length of the transport distance. The unit of measurement for the volume of goods transported is the ton (T); for pipeline transport, the unit of measurement is cubic meters (m³), but the total transported volume is converted to tons for aggregation upon calculation.
The volume of goods transported is determined based on the actual weight of the transported goods (including packaging, if any). The volume of goods transported shall be recorded after the completion of the transportation process, when the goods have been delivered to the designated delivery point in accordance with the provisions of the transport contract and after the completion of delivery procedures. For bulky goods transported by automobiles, in case the direct measurement of volume is not feasible, the volume shall be estimated at 50% of the vehicle's load capacity or determined in accordance with the agreement between the vehicle owner and the goods owner for the actual volume of the goods.
b) Volume of goods transited
The volume of goods transited refers the mass of goods transported, calculated based on the length of the transport distance.
Calculation formula:
|
Volume of goods transited (T.Km) |
= |
Volume of goods transported (T) |
x |
The transport distance (Km) |
2. Main disaggregation
- Transport industry (railway/road/waterway/airway);
- Form of economic organization;
- Domestic/foreign country;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Economic census;
- Enterprise survey;
- Survey of individual production and business establishments;
- Survey of trade and service activities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.2.1.a. Share of added value in the manufacturing and processing industry within the GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
Share of added value in the manufacturing and processing industry within the gross domestic product (GDP) means the percentage of added value created in the manufacturing and processing industry to GDP in a specified period.
Calculation formula:
|
Share of added value in the manufacturing and processing industry within the GDP |
= |
Added value in the manufacturing and processing industry |
x 100 |
|
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
In which:
|
Added value in the manufacturing and processing industry |
= |
The value of production in the manufacturing and processing industry |
- |
Intermediate costs of the processing and manufacturing industry |
2. Main disaggregation
- Form of economic organization;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Economic census;
- Enterprise survey;
- Survey of individual production and business establishments;
- Results of the statistical surveys conducted in the National statistical survey program.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.2.1.b. Per capita added value in the manufacturing and processing industry at purchasing power parity
1. Definition and calculation method
The per capita added value in the manufacturing and processing industry at purchasing power parity (PPP) shall be calculated by the added value in the manufacturing and processing industry at purchasing power parity of the year divided by the average population of the respective year.
Calculation formula:
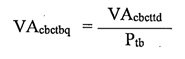
In which:
VAcbctbq: Per capita added value in the manufacturing and processing industry at purchasing power parity;
VAcbcttd: Added value in the manufacturing and processing sector at purchasing power parity.
VAcbcttd = VAcbcthh x Ttd
VAcbcthh: Added value in the manufacturing and processing sector at current price;
Ttd: The purchasing power parity exchange rate of Vietnam compared to the global average exchange rate;
Ptb: Average population in the year.
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources
- Economic census;
- Enterprise survey;
- Survey of individual production and business establishments;
- Results of the statistical surveys conducted in the National statistical survey program.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.2.2. Share of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry
1. Definition and calculation method
The share of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry means the percentage of the number of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry to the total employed labor.
Calculation formula:
|
Share of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry |
= |
Number of employed labor in the manufacturing and processing industry |
x 100 |
|
The total number of employed workers |
2. Main disaggregation Gender.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.3.2. Number of small- and medium-sized enterprises with outstanding loans at credit institutions
1. Definition and calculation method
Small- and medium-sized enterprises are classified by size, including micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises.
a) Micro-sized enterprises
Micro-sized enterprises in the sectors of agriculture, forestry and fisheries; and the sectors of industry and construction have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 10 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 3 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 3 billion.
Micro-sized enterprises in the sectors of trade and service have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 10 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 10 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 3 billion.
b) Small-sized enterprises
Small-sized enterprises in the sectors of agriculture, forestry and fisheries; and the sectors of industry and construction have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 100 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 50 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 20 billion but are not micro-sized enterprises.
Small-sized enterprises in the sectors of trade and service have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 50 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 100 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 50 billion but are not micro-sized enterprises.
c) Medium-sized enterprises
Medium-sized enterprises in the sectors of agriculture, forestry and fisheries; and the sectors of industry and construction have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 200 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 200 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 100 billion but are not not micro- and small-sized enterprises.
Medium-sized enterprises in the sectors of trade and service have an average number of employees covered by social insurance not exceeding 100 a year and the total revenue of the year not exceeding VND 300 billion or the total capital amount not exceeding VND 100 billion but are not not micro- and small-sized enterprises.
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The State Bank of Vietnam.
9.5.1. Spending on scientific research and technology development relative to GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
The spending on scientific research and technology development include expenditures for development investment, expenditures for scientific research and technological development tasks and other expenditures. The sources of funds are categorized into three types:
(1) State budget (including state budgetary sources): is divided into the central budget and the local budget. The central budget consists of funds allocated from the Ministry of Science and Technology and other ministries and sectors. The local budget is the portion balanced from the budgets of provinces and centrally-run cities;
(2) Non-state budget sources: funds from enterprises and higher education institutions (universities and colleges);
(3) Foreign sources.
The proportion of spending on scientific research and technology development to the gross domestic product is calculated using the following formula:
|
The proportion of spending on scientific research and technology development to the gross domestic product (%) |
= |
Spending on scientific research and technology development |
x 100 |
|
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
2. Main disaggregation: Sources of funding.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources
- Spending on scientific research and technology development: Survey on scientific research and technology development;
- The gross domestic product (GDP): - Statistical survey; Statistical reporting regime; Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Science and Technology;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.5.2. Number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development per 1,000,000 population
1. Definition and calculation method
An individual engaged in scientific research and technology development means the one holding a qualification of at least college degree who directly participates in and dedicates at least 10% of their working time to scientific research and technological development activities in the following sectors:
- Scientific research organizations and scientific research and technology development institutions, structured as academies, institutes, centers, laboratories, research stations, observatories, testing stations, and other forms;
- Higher education institutions and colleges, organized in accordance with the Law on Higher Education and the Law on Vocational Education;
- Scientific and technological service providers, structured as centers, offices, testing laboratories, and other forms;
- Administrative agencies and other non-business units engaged in research and development (R&D) activities;
- Enterprises conducting R&D activities.
Calculation method:
- The headcount of research personnel refers to the total number of individuals possessing a college degree or higher who directly engage in and allocate at least 10% of their working time to the scientific research and technology development activities.
- The full-time equivalent (FTE) of research personnel refers to the number of individuals possessing a college degree or higher and directly engaged in the scientific research and technology development activities that is converted into full-time equivalent time based on the proportion of working time spent on research and development during the statistical year. One FTE is an individual who dedicates 100% of their working time to research and development activities for one full year.
To calculate the number of FTEs, it is necessary to determine the time-use coefficient for scientific research and technological development of each group of individuals engaged in scientific research and technological development.
Calculation formula:
|
The number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development (FTE) |
= |
The number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development in scientific research and technology development institutions x conversion coefficient |
+ |
The number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development in universities x conversion coefficient |
+ |
The number of individuals engaged in scientific research and technology development in enterprises x conversion coefficient |
+ |
(Similarly, by area of operation), etc. |
According to the Ministry of Science and Technology’s research results in 2019, the conversion coefficients of the area of scientific research and technology development institutions, area of universities, area of administrative and non-business units, area of scientific and technological service providers, and area of enterprises are 1, 0.31, 0.22, 0.3 and 0.71, respectively. Such conversion coefficients may be changed from time to time.
2. Main disaggregation
- Professional qualifications;
- Area of operation;
- Gender;
- Science and technology sector.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Survey on scientific research and technology development.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Science and Technology.
9.c.1. Proportion of the population covered by mobile networks
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of the population covered by mobile networks means the percentage of the population within range of mobile-cellular signals to the average population of the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of the population covered by mobile networks (%) |
= |
The population covered by mobile networks |
x 100 |
|
The average population |
The population within range of mobile-cellular signals is the population within the range of signals 3G/4G/5G that meet the standards (on mobile information) in accordance with current regulations.
2. Main disaggregation
- Technology (3G/4G/5G);
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the information and communications sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Information and Communications;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
9.c.2. Proportion of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access means the percentage of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access to the total number of households of the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access (%) |
= |
Number of households with broadband fiber optic Internet access |
x 100 |
|
Total number of households |
2. Main disaggregation Province, centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the information and communications sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Information and Communications;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 10: Reducing inequality within and among societies
10.1.1.a. Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita income growth rate
1. Definition and calculation method
Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita income growth rate is determined as the ratio of (a) and (b).
(a) Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population means the ratio of the per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population in the year t compared to the one in the year t-1.
(b) Overall per capita income growth rate means the ratio of the per capita income in the year t compared to the one in the year t-1.
Calculation formula:
|
Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita income growth rate |
= |
Growth rate of per capita income of the lowest 40% of the population |
|
Overall per capita income growth rate |
2. Main disaggregation Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
10.1.1.b. Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita expenditure growth rate
1. Definition and calculation method
Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita expenditure growth rate is determined as the ratio of (a) to (b).
(a) Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population means the ratio of the per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population in the year t compared to the one in the year t-1.
(b) Growth rate of per capita expenditure means the ratio of the per capita expenditure in the year t compared to the one in the year t-1.
Calculation formula:
|
Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population compared to the overall per capita expenditure growth rate |
= |
Growth rate of per capita expenditure of the lowest 40% of the population |
|
Overall per capita expenditure growth rate |
2. Main disaggregation Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
10.2.1. Proportion of people living below 50% of the median income
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of people living below 50% of the median income means the percentage of the population whose per capita income is less than 50% of the country's median per capita income relative to the total population.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
10.4.1. Share of labor value in the GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
The share of labor value in the GDP is the percentage of payments to employees in the gross domestic product (GDP).
Payments to employees are the total amount of remuneration in cash or in kind that employers must pay for work performed by employees during the period.
Payments to workers includes:
- Salaries (in cash or in kind);
- Social insurance payments for employees (by using employer's expenses).
Calculation formula:
|
The share of labor value in the GDP (%) |
= |
The total payments to employees |
x 100 |
|
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
2. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
3. Data sources
- Statistical survey;
- Statistical reporting regime;
- Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
10.4.2. Gini coefficient of income distribution inequality
1. Definition and calculation method
The Gini coefficient is calculated based on the Lorenz curve. The Lorenz curve is constructed from two factors: the cumulative percentage of income earned by the population and the corresponding cumulative percentage of the population.
The Gini coefficient is determined by dividing the area A (formed by the Lorenz curve and the 45-degree line) by the area A+B (which represents the right triangle located under the 45-degree line from the origin).
Calculation formula:
![]()
In which:
G: The Gini coefficient;
Fi: Cumulative population percentage up to the ith individual;
Yi: Cumulative income percentage up to the ith individual.
When the Lorenz curve coincides with the 45-degree line (the line of perfect equality), the Gini coefficient equals 0 (since A = 0), indicating perfect equality of income in the society, where every individual earns the same income. When the Lorenz curve coincides with the horizontal axis, the Gini coefficient equals 1 (since B = 0), representing perfect inequality of income, where one individual receives the entire income of the society. The Gini coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, where higher values indicate higher inequality of income in the population.
The Gini coefficient is most accurate when calculated based on individual income data. However, for practical reasons and ease of computation, the Gini coefficient may also be calculated from per capita income data by population groups. The Gini coefficient calculated by population groups tends to be lower than the one calculated by individual. The larger the number of population groups considered, the more precise the Gini coefficient becomes.
2. Main disaggregation
- Urban/rural area;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
10.7.1. Recruitment cost ratio paid by migrant workers relative to their monthly income in destination countries
1. Definition and calculation method
The recruitment cost ratio paid by a migrant worker relative to his/her monthly income in the destination country is the indicator reflecting the ratio of the total cost paid by the migrant worker for his/her work in the foreign country compared to his/her average monthly income from such work in the destination country.
The reference duration: Recruitment cost and income used to calculate this indicator refer to the first job in the destination country and the first year of employment of the migrant worker in the destination country.
The cost paid by the migrant worker for his/her work in the foreign country includes any fees or costs incurred during the recruitment process for his/her first job abroad. Such cost corresponds to the total amount that the migrant worker and/or his/her family must pay in order to search for and secure employment with an employer abroad, as well as the expenses incurred to reach the workplace for the first job abroad (airfare, visa fees, travel expenses, etc.).
The income of the migrant worker in the destination country includes the amounts actually received during the most recent month for the first job in the destination country, including bonuses and other income (for example, overtime earnings), minus deducted amounts such as taxes, payment of social insurance premiums, and payroll deductions for the recovery of any recruitment cost incurred by the employer.
Because recalling the first job in the destination country may be challenging, it is recommended that the focus is on the migrant workers whose first job in the destination country occurred within a specified period (for example, for three years or fewer).
Calculation formula:
|
Recruitment cost ratio paid by migrant workers relative to their monthly income in destination countries (%) |
= |
The total cost paid by the migrant workers for their work in the foreign countries |
x 100 |
|
The migrant workers’ total average monthly income from such work in the destination countries |
2. Disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Technical or professional qualifications;
- Main destination country.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources: Labor force survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
Goal 11: Developing sustainable, resilient urban and rural areas; ensuring safe living and working environments; and rationally distributing populations and labor across regions
11.1.1. Proportion of the population living in temporary housing
1. Definition and calculation method
People living in temporary housing are those residing in dwellings constructed with simple structural materials, such as miscellaneous wood/bamboo, lime-soil/straw, planks/wattle/plywood for columns and walls, and roofs made of roofing sheets, thatch/straw/reed/tar paper.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of the population living in temporary housing (%) |
= |
The population living in temporary housing |
x 100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region;
- Income group.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Vietnam household living standards survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
11.5.1. Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people
1. Definition and calculation method
Natural disasters means abnormal natural phenomena which may cause damage to human life, property, the environment, living conditions and socio-economic activities, including: typhoon, tropical low pressure, whirlwind, lightning, heavy rain, flood, flashflood, inundation, landslide and land subsidence due to floods or water currents, water rise, seawater intrusion, extreme hot weather, drought, damaging cold, hail, hoarfrost, earthquake, tsunami and other types of natural disaster.
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people refers the number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people in a specific year.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people |
= |
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters |
x 100,000 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Type of natural disaster (tropical low pressure/typhoon/flood/flashflood/landslide/inundation/drought/extreme hot weather/damaging cold);
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the agriculture and rural development sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
11.5.2. Total economic losses caused by natural disasters
1. Definition and calculation method
Total economic losses caused by natural disasters means the total material loss, including: Housing, related facilities and infrastructure; crops, vessels, aquaculture cages, seafood farming structures, and other material assets.
2. Main disaggregation
- Group of natural disaster types;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the agriculture and rural development sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
11.6.1. Proportion of urban solid waste collected and treated
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of urban solid waste collected and treated means the percentage of the volume of urban solid waste collected and treated to the total volume of urban solid waste generated.
- The volume of domestic solid wastes collected and treated refers the mass of domestic solid wastes that is collected and transported by public utility companies, private enterprises, and waste collection teams or units, etc. and delivered to solid waste treatment facilities or landfill sites.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of urban solid waste collected and treated (%) |
= |
Volume of urban solid waste collected and treated (ton) |
x |
100 |
|
Total volume of urban solid waste generated (ton) |
2. Main disaggregation
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Survey of environment protection criteria.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
11.8.1. Proportion of communes recognized as meeting new rural standards
1. Definition and calculation method
A commune recognized as meeting new rural standards is a commune that fulfills the new rural standards and is officially recognized in writing by the Steering Committee of National Target Program on New Rural Development of the province or centrally-run city.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of communes recognized as meeting new rural standards (%) |
= |
Number of communes recognized as meeting new rural standards |
x |
100 |
|
Total number of communes implementing the National Target Program on New Rural Development |
2. Main disaggregation: Province, centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
11.8.2. Proportion of rural solid waste collected and treated
1. Definition and calculation method
- Proportion of rural solid waste collected and treated means the percentage of the volume of rural solid waste collected and treated to the total volume of rural solid waste generated.
- The volume of domestic solid wastes collected and treated refers the mass of domestic solid wastes that is collected and transported by public utility companies, private enterprises, and waste collection teams or units, etc. and delivered to solid waste treatment facilities or landfill sites.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of rural solid waste collected and treated (%) |
= |
Volume of rural solid waste collected and treated (ton) |
x |
100 |
|
Total volume of rural solid waste generated (ton) |
2. Main disaggregation
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Survey of environment protection criteria;
- Statistical reporting regime of the natural resources and environment sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Goal 12: Ensuring sustainable production and consumption patterns
12.4.2. Proportion of hazardous waste collected and treated
1. Definition and calculation method
Wastes means physical substances in solid, liquid, gaseous or whatever form discharged from production, business, service, daily-life or other activities.
Hazardous wastes means wastes containing toxic, radioactive, contagious, flammable, explosive, abrasive, poisonous or otherwise harmful elements.
Proportion of hazardous waste collected and treated means the percentage of the volume of hazardous waste collected and treated (also including recycling, co-processing, and energy recovery from such waste) to the total volume of hazardous waste generated.
The higher this ratio, the better the level of environmental protection, and vice versa.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of hazardous waste collected and treated (%) |
= |
Volume of hazardous waste collected and treated (ton) |
x |
100 |
|
Total volume of hazardous waste generated (ton) |
2. Main disaggregation
Collection/Treatment.
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Survey of environment protection criteria.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Industry and Trade; the Ministry of Health.
12.4.3. Proportion of polluted land areas remediated, rehabilitated, and restored according to regulations
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of polluted land areas remediated, rehabilitated, and restored means the percentage of the total of polluted land areas completely remediated and rehabilitated to the total polluted land areas detected up to the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of polluted land areas remediated, rehabilitated, and restored according to regulations (%) |
= |
Total of polluted land areas completely remediated and rehabilitated (point) |
x |
100 |
|
Total of polluted land areas detected |
In which:
A polluted land area is an area discovered to contain one or more residual pollutants exceeding environmental technical regulations, adversely affecting humans, the environment, and ecosystems.
Polluted land area included in this indicator comprise: farmland contaminated by chemicals or pesticides; areas polluted by chemical warfare agents; areas where the mining of toxic minerals has ended; land areas within centralized production, business, and service zones, industrial clusters, chemical production establishments, chemical storehouses, pesticides storehouses determined to have residual contamination; craft villages, landfill sites failing to meet sanitary requirements that have operations ceased or have been closed.
2. Main disaggregation
- Type of polluted land area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime of the natural resources and environment sector;
- Survey of environment protection criteria.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Goal 13. Taking timely, effective action against climate change and natural disasters
13.1.1. Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people
1. Definition and calculation method
Natural disasters means abnormal natural phenomena which may cause damage to human life, property, the environment, living conditions and socio-economic activities, including: typhoon, tropical low pressure, whirlwind, lightning, heavy rain, flood, flashflood, inundation, landslide and land subsidence due to floods or water currents, water rise, seawater intrusion, extreme hot weather, drought, damaging cold, hail, hoarfrost, earthquake, tsunami and other types of natural disaster.
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people refers The number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people in a specific year.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters per 100,000 people |
= |
Number of deaths, missing persons, and injuries due to natural disasters |
x |
100,000 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Type of natural disaster (tropical low pressure/typhoon/flood/flashflood/landslide/inundation/drought/extreme hot weather/damaging cold);
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the agriculture and rural development sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis:
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
13.2.2. Per capita greenhouse gas emissions
1. Definition and calculation method
Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that contributes to the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is the phenomenon whereby the Sun’s radiant energy is absorbed in the atmosphere, converted into heat, and leads to global warming. According to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, the principal greenhouse gases include: CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs, PFCs, SF6, NF3.
Annual greenhouse gas emissions in a year are converted into CO2-equivalent amounts, with data collected on a nationwide scale.
Calculation formula:
|
Per capita greenhouse gas emissions (tons of CO2 equivalent/person) |
= |
The total greenhouse gas emissions converted into CO2 equivalent amount |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Type of gas emission;
- Emission source.
3. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources
- National statistical reporting regime;
- Statistical reporting regime of the natural resources and environment sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the Ministry of Construction, the Ministry of Industry and Trade, the Ministry of Transport, and People's Committees of provinces and centrally-run cities.
13.3.1.a. Proportion of greenhouse gas-emitting facilities with emission reduction plans implemented
1. Definition and calculation method
Greenhouse gas-emitting establishments subject to making of greenhouse gas inventories are those emitting an annual amount of greenhouse gases of 3,000 tons of CO2 equivalent or more or falling into one of the following cases:
- A thermal power plant or an industrial production establishment consuming a total annual energy amount of 1,000 tons of oil equivalent (TOE) or more;
- A cargo transport company consuming a total annual fuel amount of 1,000 TOE or more;
- A commercial building consuming a total annual fuel amount of 1,000 TOE or more; or,
- A solid waste treatment facility with an annual operational capacity of 65,000 tons or more.
The list of greenhouse gas-emitting establishments subject to making of greenhouse gas inventories is defined by the Prime Minister and must be updated every two years.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of greenhouse gas-emitting facilities with emission reduction plans implemented |
= |
Number of greenhouse gas-emitting establishments subject to making of greenhouse gas inventories |
x |
100 |
|
Number of greenhouse gas-emitting establishments subject to making of greenhouse gas inventories |
2. Publication frequency: Every 2 years.
4. Data sources: Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
13.3.2. Proportion of the population educated on disaster prevention and control
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of the population educated on disaster prevention and control means the percentage of the population educated on disaster prevention and control to the total population.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of the population educated on disaster prevention and control (%) |
= |
The population educated on disaster prevention and control |
x |
100 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources:
- Statistical reporting regime of the agriculture and rural development sector;
- Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
Goal 14. Conserving and sustainably using oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development
14.1.1.a. Proportion of coastal water monitoring points meeting national technical standards for organic pollution (N-NH4+) and mineral oil
1. Definition, calculation method
The inshore sea area for management of marine water quality is the maritime zone (also including lagoon areas) extending seaward 6 nautical miles from the shoreline (approximately 10.8 km).
Substances present in the marine environment of which the measured specifications exceed thresholds defined by national technical regulations are capable of polluting the marine environment and adversely affecting marine species and ecosystems.
Within the national environmental monitoring system, the marine environment monitoring program (covering the water environment in estuaries, coastal areas, offshore seas), marine water quality is assessed through several principal parameters such as salinity, DO, N-NH4+, N-NO3-, P-PO43-, CN, heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Hg), oil and grease, and chlorophyll-a. The concentrations of these substances in seawater are the measured specifications of those substances existing in the seawater.
Within the scope of this indicator, the proportion of the coastal water monitoring points meeting national technical standards is only considered for the parameters of organic pollution (N-NH4+) (%) and mineral oil (%).
N-NH4+ is one of the characteristic parameters indicating nutrient pollution in the marine environment. If the marine environment contains high concentrations of these nutrients, red tides may occur, causing rot and unpleasant odors in the marine environment.
Mineral oil in water refers to the amount of oil present in the marine environment caused by human activities; if the concentration of oil in seawater exceeds thresholds defined by national technical regulations, it will pollute the marine environment and adversely affect aquatic species.
The specifications and limit values are stipulated in the National Technical Regulation on Marine Water Quality (QCVN 10:2023/BTNMT), issued by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
The method used to determine the concentrations of certain substances in seawater is to collect water samples at monitoring locations and then analyze the results in a laboratory.
The method of sampling for marine water quality monitoring shall comply with the guidelines of corresponding national technical regulations and standards.
The method of analyzing and determining parameters in seawater is shall comply with the guidelines of national standards or equivalent analytical standards of international organizations.
The data used for statistical reporting on this indicator are the monitoring data of the parameters which is equal to the average values of the monitoring periods during the year.
The proportion of coastal water quality parameters meeting the requirements of the national technical regulations is the ratio of coastal water quality parameters at the time of sampling to the coastal water quality parameters meeting the requirements of the relevant national technical regulations.
Depending on the coastal water quality parameters, the ratio of assessment of coastal water quality meets or fails to meet the national technical regulations.
2. Publication frequency: Annually
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
14.5.1. Proportion of marine and coastal protected areas relative to the total national marine area
1. Definition and calculation method
Marine protected areas aim to safeguard ecosystems and aquatic species bringing economic and scientific values, contributing to the development of the marine economy and improving the livelihoods of fishing communities in coastal localities.
The area of marine protected areas refers to the area of the sea, islands, archipelagos, and coastal zones within these marine protected areas for the purpose of conserving marine biodiversity.
Proportion of marine and coastal protected areas relative to the total national marine area refers to the percentage of marine and coastal protected areas compared to the total national marine area.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of marine and coastal protected areas relative to the total national marine area (%) |
= |
Area of marine and coastal protected areas relative to the total national marine area |
x |
100 |
|
The total national marine area |
2. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
Goal 15: Protecting and sustainably developing forests, conserving biodiversity, enhancing ecosystem services, combating desertification, preventing degradation, and restoring land resources
15.1.1. Forest coverage ratio
1. Definition and calculation method
Forest coverage ratio means the percentage of the forest area to the total natural land area in a certain geographical area.
Calculation formula:
|
Forest coverage ratio (%) |
= |
Existing forest area |
x |
100 |
|
The total natural land area |
2. Main disaggregation
- Origin of forest formation: Natural forest and planted forest;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Forest changes monitoring survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
15.1.2. Proportion of terrestrial protected areas relative to the total territorial land area
1. Definition and calculation method
Nature conservation zone means a geographical area that has fixed boundaries and functional sections for biodiversity conservation.
Protected areas include national parks, nature reserves, species/habitat conservation zones, landscape conservation zones, etc. recognized in provinces and centrally run cities.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of terrestrial protected areas relative to the total territorial land area (%) |
= |
The terrestrial protected areas |
x |
100 |
|
The total territorial land area |
2. Main disaggregation: Province, centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources: Survey of environment protection criteria.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
15.2.1a. Area of forests under protection
1. Definition and calculation method
Area of forests under protection is the area of forests that have been allocated or contracted to organizations, individuals, or households for management and protection in combination with appropriate exploitation, aimed at preventing harmful actions against forests such as deforestation for swidden cultivation, illegal harvest of forest products, and unauthorized wildlife hunting.
Area of forests under protection includes the area of production forests, protection forests and special-use forests that have been allocated or contracted to forest owners for protection, to a specified point in time.
2. Main disaggregation
- By use purpose: special-use forest, protection forest, production forest.
- by form of economic organization: state economy; non-state economy; economy with foreign direct investment.
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Forest changes monitoring survey.
- Statistical reporting of the forestry sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
15.3.1. Proportion of degraded land area
1. Definition and calculation method
Degraded land refers to the land of which initial inherent properties and characteristics see negative changes due to impacts of natural conditions or humans.
Land degradation is capable of occurring on all types of land: agricultural land, forestry land, land for aquaculture, unused flatland, unused hilly and mountainous land.
Degraded land of the following types of degradation: Land suffering drought and desertification; land becoming barren; landslides; land clumping or laterization; soil becoming hardened and compacted; soil pollution; soil erosion; waterlogged land; land salinization; land alkalization.
Calculation formula:
|
The total degraded land area |
= |
Area of slightly degraded land |
+ |
Area of moderately degraded land |
+ |
Area of severely degraded land |
Synthesis of the classification of land degradation levels (severely degraded land, moderately degraded land, slightly degraded land) in accordance with the technical regulations on land degradation investigation of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
|
Proportion of degraded land area (%) |
= |
The total degraded land area |
x |
100 |
|
The total land area |
2. Main disaggregation
- Type of degradation;
- Type of land (agricultural land/ forestry land/ land for aquaculture/ unused flatland/ unused hilly and);
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime of the natural resources and environment sector;
- Survey and assessment of land degradation of socio-economic regions; provinces and centrally-run cities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
15.6.1. Proportion of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge on genetic resources
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge on genetic resources means the percentage of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge on genetic resources to the total number of provinces and centrally-run cities.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge on on genetic resources |
= |
Number of provinces and centrally run cities participating in the national database on genetic resources and traditional knowledge on genetic resources |
x |
100 |
|
Total number of provinces and centrally-run cities |
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
15.6.2. Number of applications for access to genetic resources and benefit-sharing
1. Definition and calculation method
Genetic resource includes all species and genetic specimens in nature, conservation zones, biodiversity conservation facilities and scientific research and technological development institutions and in nature. In which, genetic specimen means any specimen of plant, animal, microorganism or fungus that possesses functional units of heredity which can regenerate.
Access to genetic resources means activities of investigating and collecting genetic resources for research and development and production of commercial products.
Mutually Agreed Terms means an agreement between the Provider of genetic resources and the User on the terms and conditions of access and use and the benefits to be shared between both parties.
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Goal 16: Promoting peaceful, just, and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all, and building accountable and participatory institutions at all levels
16.1.1. Number of victims of intentional homicide per 100,000 people
1. Definition and calculation method
Intentional homicide means the act of homicide of which the offender is well aware that his/her act is socially dangerous and wishes such consequence to occur.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of victims of intentional homicide per 100,000 people (%) |
= |
Number of victims of intentional homicide |
x |
100,000 |
|
Total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Public Security;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.1.3. Proportion of the population affected by violence
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of the population affected by violence means the percentage of the population affected by violence to the total population.
The population affected by violence includes those suffering physical violence, sexual violence and mental violence.
- Physical violence consists of acts intended to cause physical harm to the victim. Physical violence includes the acts of forcible assault, acts of causing or risking physical injury such as pushing, tearing out hair, slapping, kicking, biting or the use of weapons to attack, etc.
- Sexual violence is any unwanted sexual act or an attempt to obtain an unwanted sexual act from the victim, without the victim’s consent or through the use of force, threats, or abuse of power/position to force the victim to consent to such sexual act; etc.
- Psychological violence is any act or statement of a threatening or insulting nature, unlawful control, destruction of property, or any conduct causing mental harm to the victim.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of the population affected by violence (%) |
= |
The number of persons affected by violence |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Type of violence (physical violence/sexual violence/ mental violence);
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.1.4. Proportion of the population feeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of the population feeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark means the percentage of the number of persons eeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark to the total population.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of the population feeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark (%) |
= |
The number of persons feeling safe walking alone around their neighborhood after dark |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.2.1. Proportion of individuals under 18 who have experienced physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month
1. Definition and calculation method
Physical punishment is any act that causes physical discomfort or pain but not to the extent of causing injury.
Emotional punishment is any act of yelling, scolding, etc. that humiliates or insults a child.
Proportion of individuals under 18 who have experienced physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month means the percentage of individuals under 18 who have experienced any physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month to the total number of individuals under 18 surveyed.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of individuals under 18 who have experienced physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month (%) |
= |
The number of individuals under 18 who have experienced any physical or emotional punishment by caregivers in the past month |
x |
100 |
|
The total number of individuals under 18 surveyed |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.2.2. Number of victims of human trafficking detected per 100,000 people
1. Definition and calculation method
Victims of human trafficking mean the persons harmed by acts of human trafficking or the trafficking in persons aged under 16 years stipulated in Articles 150 and 151 of the Penal Code.
This indicator is calculated by the number of victims of human trafficking detected per 100,000 people within the same period.
Detected victims are identified as such by competent authorities as a result of rescue operations, repatriation, or are those who return, report on their own and are officially recognized as victims by competent agencies.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of victims of human trafficking detected per 100,000 people (%) |
= |
Number of victims of human trafficking detected |
x |
100,000 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Annually
4. Data sources: Administrative data.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Public Security;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.2.3. Proportion of individuals aged 18-29 who experienced sexual violence before the age of 18
1. Definition and calculation method
Sexual violence against individuals under 18 years of age includes any compelled sexual activity committed by an adult against a child, who is entitled to protection under penal law, comprising:
a) The enticement or coercion of a child to engage in any unlawful or psychologically harmful sexual activity;
b) The use of children in commercial sexual exploitation;
c) The use of children in sound images or images depicting child sexual abuse;
d) Child prostitution, sexual slavery, sexual exploitation in tourism, child trafficking for the sexual exploitation (within and between countries), child trafficking for sexual purpose and forced marriage..
Proportion of individuals aged 18-29 who experienced sexual violence before the age of 18 means the percentage of reported individuals aged 18-29 who experienced any sexual violence before the age of 18 to the total number of individuals aged 18-29 surveyed.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of individuals aged 18-29 who experienced sexual violence before the age of 18 (%) |
= |
Number of reported individuals aged 18-29 who experienced any sexual violence before the age of 18 |
x |
100 |
|
The total number of individuals aged 18-29 surveyed |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Marital status;
- Level of education;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.3.1. Proportion of victims of violence in the past 12 months who reported the incident to competent authorities or supportive organizations
1. Definition and calculation method
Victims of violence include those suffering physical violence, sexual violence and psychological violence.
- Physical violence consists of acts intended to cause physical harm to the victim. Physical violence includes the acts of forcible assault, acts of causing or risking physical injury such as pushing, tearing out hair, slapping, kicking, biting or the use of weapons to attack, etc.
- Sexual violence is any unwanted sexual act or an attempt to obtain an unwanted sexual act from the victim, without the victim’s consent or through the use of force, threats, or abuse of power/position to force the victim to consent to such sexual act; etc.
- Psychological violence is any act or statement of a threatening or insulting nature, unlawful control, destruction of property, or any conduct causing mental harm to the victim.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of victims of violence in the past 12 months who reported the incident to competent authorities or supportive organizations (%) |
= |
Number of victims of violence in the past 12 months who reported the incident to competent authorities or supportive organizations |
x |
100 |
|
Total number of victims of violence in the past 12 months |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Type of violence;
- Urban/rural area.
3. Publication frequency: Every 10 years.
4. Data sources: Population health and life experience survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
16.4.2. Total number of confiscated illegal weapons, explosives, and support tools
1. Definition and calculation method
Weapons, explosive materials and support tools include:
a) Weapon means an equipment or a combination of equipment that is manufactured and produced to inflict injury or harm to human life and health and destroy material structures, including military-use weapons, rudimentary weapons, sporting weapons, hunting rifles.
b) Explosive means a product causing quick and strong chemical reactions that spread heat, produce gases, generate light and cause explosions due to impacts of the initial stimulus, including:
- Dynamite which means chemicals or compounds used for creating explosive reaction due to impacts of the initial stimulus;
- Explosive accessories including detonators, detonating wires, slow-burning wires, explosive-containing articles providing the initial stimulus which burst explosives or specialized equipment containing explosives.
c) Support tools means equipment or military animals used for carrying out official duties and providing protection, which aims to reduce and prevent the violators from resisting or running way, protect people on duties, people performing protection missions or giving signals of emergency, including:
- Stun guns, guns shooting asphyxiant gas, guns shooting poisons, tranquillizer guns, coilguns, net guns; rope launchers; guns using plastic bullets, guns using exploding bullets, guns using rubber bullets, tear gas, flares, tracers and ammunition used for these types of guns; devices used for spraying tear gas, asphyxiant gas, poisons, anesthetics or itching powder; smoke grenades, tear gas grenades; stun batons, rubber batons, metal batons; figure-8 handcuffs, spike-boards, barbed wires; armors; electric gloves, knife gloves; shields, bulletproof helmets; sonic weapons;
interrogation chairs for special subjects as listed in the catalog issued by the Minister of Public Security.
- Military animals which are animals trained and used for protecting national security and ensuring social order and safety, in the list issued by the Minister of Public Security;
- Other devices with similar properties and effects support tools defined in Point a of this Clause, other than those in the list issued by the Minister of Public Security.
This indicator considers only the number of confiscated illegal weapons, explosives, and support tools to assess the level of public safety and the threat to social security.
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Public Security;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of National Defence.
16.5.1. Proportion of individuals paying informal costs to access public services
1. Definition and calculation method
Public services mean the activities serving the common and essential interests, and the basic rights and obligations of organizations and citizens, performed directly by the State or delegated to non-state entities, for the purposes of efficiency and fairness. Public services are activities of State agencies in performing the function of State administrative management and ensuring the provision of public goods to meet the society’s common and essential needs. Such activities may be carried out by either the State or private entities.
The proportion of individuals paying informal costs to access public services refers the percentage of individuals paying informal costs to access public services compared to the total number of individuals accessing public services surveyed.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of individuals paying informal costs to access public services (%) |
= |
Number of individuals subject to payment of informal costs to access public services |
x |
100 |
|
Total number of individuals accessing public services surveyed |
2. Main disaggregation
- Age group;
- Gender;
- Type of formal service;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical survey (Survey on citizens’ satisfaction with state administrative agencies’ services).
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Home Affairs.
16.5.2. Proportion of businesses paying informal costs to access public services
1. Definition and calculation method
Public services mean the activities serving the common and essential interests, and the basic rights and obligations of organizations and citizens, performed directly by the State or delegated to non-state entities, for the purposes of efficiency and fairness. Public services are activities of State agencies in performing the function of State administrative management and ensuring the provision of public goods to meet the society’s common and essential needs. Such activities may be carried out by either the State or private entities.
The proportion of businesses paying informal costs to access public services refers the percentage of businesses paying informal costs to access public services compared to the total number of businesses using public services that were surveyed.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of businesses paying informal costs to access public services (%) |
= |
Number of businesses subject to payment of informal costs to access public services |
x |
100 |
|
Total number of businesses accessing public services surveyed |
2. Main disaggregation: Province, centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Vietnam Chamber of Commerce and Industry.
16.6.1. Proportion of public budget expenditure compared to the approved budget estimate
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of public budget expenditure compared to the approved budget estimate reflects the discrepancy between the total actual state budget expenditure and the state budget estimates decided by the National Assembly; it is measured by the ratio of finalized state budget expenditure to the state budget expenditure estimates decided by the National Assembly.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of public budget expenditure compared to the approved estimate (%) |
= |
The finalized state budget expenditure |
x |
100 |
|
The state budget expenditure estimates decided by the National Assembly |
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: State budget data that has been converted according to Government finance statistics (GFS) for provision to international organizations and for disclosure on the Ministry of Finance’s Portal.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Finance.
16.6.2. Proportion of population satisfied with their last experience of public services
1. Definition and calculation method
Public services mean the activities serving the common and essential interests, and the basic rights and obligations of organizations and citizens, performed directly by the State or delegated to non-state entities, for the purposes of efficiency and fairness. Public services are activities of State agencies in performing the function of State administrative management and ensuring the provision of public goods to meet the society’s common and essential needs. Such activities may be carried out by either the State or private entities.
Public services comprise three categories: public services in the non-business sector, public services in the public-utility sector, and public services in the State administrative sector (also known as public administrative services).
Public non-business services include activities of providing essential social welfare for the people, such as education, culture, science, healthcare, sports, insurance, and social security, etc.
Public utility services are activities of supplying fundamental and essential goods and services to the people and the community, such as environmental sanitation, waste treatment, provision of clean water, urban public transportation, and natural disaster prevention and control, etc. Certain activities may be undertaken by the private sector, such as environmental sanitation and the provision of clean water.
Public administrative services are those directly connected with the State management function to meet citizens’ needs. They represent a portion of the State management function. For such function, the State must carry out direct service activities such as the issuance of permits, certificates, registrations, notarization, visas, and civil status documentation, etc.
Proportion of population satisfied with their last experience of public services means the percentage of population satisfied with their last experience of public services to the total population surveyed.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of population satisfied with their last experience of public services (%) |
= |
Population satisfied with their last experience of public services |
x |
100 |
|
The total population surveyed |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Income group;
- Persons with disabilities;
- Ethnicity;
- Type of public services;
- Urban/rural area;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical survey.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Home Affairs.
16.9.1. Proportion of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered
1. Definition and calculation method
Children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered refer the number of children under 5 years of age counted from the date of birth, whose births have been registered and have birth certificate issued in accordance with the Law on Civil Status.
Proportion of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered means the percentage of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered compared to the total number of children under 5 years of age in the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered (%) |
= |
Number of children under 5 years of age whose births have been registered |
x |
100 |
|
Number of children under 5 years of age |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
For the disaggregation of ethnicity, the publication frequency is every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Inter-censal population and housing survey;
- Population change and family planning survey;
- National population database;
- Electronic civil status database;
- Specialized population data warehouse.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency:
+ The Ministry of Public Security;
+ The Ministry of Health: Provide the specialized population data warehouse;
+ The Ministry of Justice: Provide the electronic civil status database.
Goal 17: Strengthening the means of implementation and revitalizing the global partnership for sustainable development
17.1.1 Total state budget revenue as a proportion of GDP
1. Definition and calculation method
This indicator reflects state budget revenue mobilization relative to GDP, comprising two components: (i) The ratio of government revenue and aid to GDP, and (ii) The ratio of tax and charge revenue to GDP.
Total government revenue as a proportion of GDP means the percentage of the government revenue to the gross domestic product.
Calculation formula:
|
Total government revenue as a proportion of GDP (%) |
= |
Total government revenue |
x |
100 |
|
The gross domestic product (GDP) |
The government revenue includes: All revenues from taxes and fees; all charges for services provided by State agencies, these charges may be deducted for agencies that have to pay their operation expenses at a pre-fixed level; charges collected from service activities performed by public non-business units and state-owned enterprises, which are remitted to the State budget in accordance with the law regulations; non-refundable aid granted by foreign governments, organizations, or individuals to the Government of Vietnam and local authorities; and any other revenues as prescribed by law regulations.
Note: Both indicators of the total state budget revenue and gross domestic product are calculated at current prices.
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources
- State budget revenues: State budget data that has been converted according to Government finance statistics (GFS) for provision to international organizations and for disclosure on the Ministry of Finance’s Portal;
- The gross domestic product (GDP): - Statistical survey; Statistical reporting regime; Administrative data.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Finance.
17.1.2. Proportion of domestic budget funded by domestic taxes
1. Definition and calculation method
This indicator reflects the proportion of state budget expenditures (including investment and recurrent expenditures) that are covered by revenue from taxes and charges (excluding revenue from land use levies, proceeds from the sale of state-owned housing, and aid funds). It is measured as the ratio of tax and charge revenue to the total state budget expenditures.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of domestic budget funded by domestic taxes (%) |
= |
Tax and charge revenue |
x |
100 |
|
Total state budget expenditures |
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: State budget data that has been converted according to Government finance statistics (GFS) for provision to international organizations and for disclosure on the Ministry of Finance’s Portal.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Finance.
17.3.1.a. Official development assistance and concessional loans of foreign donors
1. Definition and calculation method
a) Definition
- Official development assistance (ODA) or concessional loan means a loan provided by a foreign donor to the State or the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam to support development activities and ensure social welfare and security.
- Counterpart fund means a fund amount contributed by the Vietnamese partner (in kind or in cash) to an ODA or concessional loan-funded program or project for preparing and implementing the program or project, which is allocated from the central budget or local budget, provided by the project owner by itself/himself/herself, contributed by beneficiaries, or allocated from other lawful funding sources.
- Governing agency: Clause 7 Article 3 of the Government’s Decree No. 114/2021/ND-CP dated December 16, 2021, on the management and use of official development assistance (ODA) and concessional loans of foreign donors.
- ODA and concessional loans of foreign donors include 3 types as follows:
+ Non-refundable ODA, which is an ODA amount not required to be refunded to the foreign donor and provided in the form of an independent project or a project in combination with ODA or concessional loan-funded investment projects.
+ ODA loan, which is a foreign loan with the grant element of at least 35%, for binding loans related to goods procurement and service provision under regulations of the foreign donor, or of at least 25%, for non-binding loans.
+ Concessional loan, which is a foreign loan which has more preferential conditions compared to a commercial loan but has the grant element not yet satisfying the criterion of an ODA loan.
- ODA and concessional loans from donors are classified according to the following criteria:
+ ODA and concessional loans from donors of which the conclusion is classified by donor.
+ ODA and concessional loans from donor of which the conclusion is classified by sectors or fields prioritized for use of ODA or concessional loans of donors.
+ ODA and concessional loans of donors of which the performance is classified by sectors or fields prioritized for use of ODA or concessional loans of donors
- Annual plan: refers to the plan approved and assigned by the competent authority to carry out activities of the programs or projects in the reporting year.
b) Calculation method
|
The total investment of the project |
= |
ODA loans |
+ |
Concessional loans |
+ |
Non-refundable aid |
+ |
Counterpart fund |
|
Foreign fund |
= |
ODA loans |
+ |
Concessional loans |
+ |
Non-refundable aid |
- Cumulative disbursement of ODA and concessional loans from project inception to the reporting date refers to the total disbursed ODA and concessional loan funds from the start of the project up to the reporting date.
- Cumulative disbursement of ODA and concessional loans from the beginning of the year to the reporting date refers to the total disbursed ODA and concessional loan funds from the start of the year up to the reporting date.
- Cumulative disbursement of counterpart funds from project inception to the reporting date refers to the total disbursed counterpart funds from the start of the project up to the reporting date.
- Cumulative disbursement of counterpart funds from the beginning of the year to the reporting date refers to the total disbursed counterpart funds from the start of the year up to the reporting date.
- Foreign capital converted to USD: The exchange rate used for conversion is the one applied at the time of project approval, as stated in the decision on project approval.
2. Main disaggregation
- Form of supports (non-refundable ODA, ODA loans, concessional loans);
- Economic sector;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Statistical reporting regime for governing agencies using ODA capital and concessional loans of donors;
- Statistical reporting regime of the planning and investment sector;
- Statistical reporting regimes of ministries, ministerial-level agencies, inter-sectoral agencies such as: the Ministry of Finance, the State Bank of Vietnam, the State Treasury of Vietnam, etc.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment.
17.3.1.b. Foreign direct investments in Vietnam
1. Definition and calculation method
Foreign investment capital is all legal funds or assets introduced into Vietnam by foreign investors to conduct investment activities in accordance with the Law on Investment and other relevant law regulations.
Registered investment capital includes:
- Newly registered investment capital from new investment projects for which an investment registration certificate has been issued during the period;
- Adjusted investment capital, which is investment capital added or reduced of projects for which an investment registration certificate has been issued previously;
- The value of capital contributions, share purchased, and capital contribution purchased by foreign investors in economic organizations.
2. Main disaggregation
- Economic sector;
- Country/territory conducting the investment;
- Province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources
- Reporting regime on foreign investment activities in Vietnam;
- Statistical reporting regime of the planning and investment sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment.
17.4.1. National external debt service as a proportion of exports of goods and services
1. Definition and calculation method
National external debt service as a proportion of exports of goods and services is the percentage of the national external debt services (excluding under-12-month principal debt service) to the export turnover of goods and services. National foreign debts in this indicator means the foreign debts of the Government, government-guaranteed foreign debts and debts borrowed and paid by enterprises and credit institutions themselves under the law regulations of Vietnam.
Calculation formula:
|
National external debt service as a proportion of exports of goods and services (%) |
= |
National external debt service (excluding under-12-month principal debt service) |
x |
100 |
|
Total export turnover of goods and services |
2. Publication frequency: Annually.
3. Data sources: Vietnam’s public debt data managed by the Ministry of Finance through the use of DMFAS software and the consolidation of statistical reports of relevant agencies.
4. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Finance.
17.6.1. Number of broadband Internet subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
1. Definition and calculation method
The number of broadband Internet subscriptions comprises both fixed broadband Internet subscriptions and mobile broadband Internet subscriptions that remain in service to the end of the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Number of broadband Internet subscriptions per 100 inhabitants (%) |
= |
Number of broadband Internet subscriptions |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Connection method (fixed/mobile);
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Statistical reporting regime of the information and communications sector.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Information and Communications;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
17.8.1. Proportion of individuals using the Internet
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of individuals using the Internet means the percentage of individuals using the Internet compared to the total population in the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of individuals using the Internet (%) |
= |
Number of individuals using the Internet |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
Individuals using the Internet are those who access the Internet to read news, search for information, participate in social networks, shop online, use online public administrative services, etc., through computers, mobile phones, tablets, gaming consoles, or digital televisions.
Depending on the management requirements of each period and to ensure international comparability, the number of individuals using the Internet is defined according to a certain age range and usage frequency. Therefore, the scope of data collection will be specifically stipulated in each survey plan.
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Age group;
- Ethnicity;
- Persons with disabilities (every 5 years);
- Urban/rural area;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
For the disaggregation of persons with disabilities, the publication frequency is every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Vietnam household living standards survey;
- National survey on persons with disabilities.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
17.11.1. Value of exports and imports
1. Definition and calculation method
a) Definition
a.1) Exports are all goods of domestic origin and re-exported goods sent abroad, reducing Vietnam’s material resources. In which:
- Goods of domestic origin are those exploited, produced or processed domestically under Vietnam’s regulations on goods origin;
- Re-exported goods are those of foreign origin that had previously been imported and recorded as imports, and then re-exported in the same state as previously imported or after being simply processed, preserved and repackaged without changing their basic characteristics.
a.2) Imports are all goods of foreign origin and re-imported goods brought into the country, increasing Vietnam’s material resources.
- Goods of foreign origin are those exploited, produced or processed abroad under Vietnam’s regulations on goods origin;
- Re-imported goods are those exported by Vietnam and recorded as exports, and then re-imported in the same state as previously exported or after being simply processed, preserved and repackaged without changing their basic characteristics.
b) Statistical scope
b.1) Goods to be included in import and export statistics of Vietnam include:
(1) Goods purchased/sold under ordinary commercial contracts concluded with foreign parties;
(2) Goods bartered to foreign countries without using the methods of payment;
(3) Goods under processing or assembly contracts concluded with foreign countries, whether or not ownership is transferred, including: Finished products returned after processing or assembly; exported or imported materials and supplies for processing or assembly; sample goods used for processing or assembly; machinery and equipment directly serving processing or assembly, as agreed upon in the processing or assembly contracts;
(4) Goods involved in transactions between a parent enterprise and its subsidiary or a directly invested branch located abroad, as well as goods transacted between a buyer and a seller who have a special relationship;
(5) Re-exported or re-imported goods; Goods of foreign origin/Vietnam's goods imported/exported and recorded as imports/exports, and then re-exported/re-imported in the same state as previously imported/exported or after being simply processed, preserved and repackaged without changing their basic characteristics, except for goods temporarily imported/temporarily exported under the inspection and supervision of Customs agencies, and are required by law regulations to be re-exported/re-imported;
(6) Exports or imports in the form of governmental or non-governmental loans or aid, loans or aid from international organizations, as well as other forms of humanitarian assistance;
(7) Goods under financial leasing contracts (machinery, equipment, means of transport) whereby lessees assume benefits, responsibilities, risks, etc. in relation to goods. For contracts containing unclear contents on these issues, the lease term of 12 months or longer will be based on;
(8) Returned goods in export or import business (goods that were recorded previously as exports or imports, then re-imported or re-exported);
(9) Goods temporarily imported or temporarily exported within given periods of time for temporary use for a specific purpose, which are then reclassified under a different customs procedure so that they are not actually re-exported or re-imported. Such goods include: those intended for display at fairs, exhibitions, product showcases; documentation for conferences, seminars, scientific research, education, sports competitions, cultural performances, art performances, medical examination and treatment, product development and research; means of transport, containers, and transport-related equipment; and other movable properties;
(10) Goods purchased or sold, or exchanged as border gifts, without a commercial contract;
(11) Specific goods:
- Non-monetary gold: gold powder, bars, bullions, pieces, coins, jewelry, etc. whether refined, raw, or semi-processed that are imported or exported by enterprises or commercial banks (excluding banks or other organizations authorized by the State Bank of Vietnam) for commercial, processing, fashioning, etc. purposes in accordance with law regulations;
- Unissued banknotes, securities, coins not for circulation or not in circulation; collections of coins or banknotes;
- Information and image storage media: Magnetic tapes and discs, CD-ROMs, smart cards, etc., whether recorded with sounds, images or not, or data, electronic games, softwares for general use purposes or normal commercial purposes (excluding those produced upon specific request of customers or original films, artworks, television programs, art performance, etc.);
- Goods dispatched or received by post or express delivery service;
- Exported or imported electricity;
- Exported or imported goods via e-commerce: The exchange of information, placement of orders, conclusion of commercial contracts and payment with foreign countries are carried out through the Internet but goods are taken out of or brought into Vietnam’s territory and go through normal customs procedures, such goods are included in the statistics if they fall within the statistical scope;
- Goods and fuels sold to foreign means of transport for use in international journeys; goods and fuels purchased for use in international journeys;
- Crude oil and minerals extracted within the continental shelf, exclusive economic zone of Vietnam, international waters, or overlapping zones where the trading with foreign countries is permitted;
- Drilling platforms sold or purchased offshore by enterprises, without undergoing customs declaration;
- Aircraft, vessels, and other vehicles involved in transactions in which customs declaration procedures are not carried out;
- Goods received from international organizations abroad or sent to international organizations (excluding goods sent or received among international organizations themselves);
- Goods that constitute personal effects, or luggage of individuals exiting or entering the country, which must be declared in accordance with regulations;
- Waste and scrap having commercial value;
- Satellites in cases where there is a change of ownership between domestic and foreign organizations or individuals.
b.2) Goods to be excluded from import and export statistics of Vietnam include:
(1) Goods exported or imported on spot: Goods purchased or sold by a Vietnamese trader under a contract with a foreign trader, but delivered or received in Vietnam as designated by the foreign trader.
(2) Goods purchased by Vietnamese traders from foreign countries and sold directly to a third country, goods that do not enter Vietnam, or goods that do enter Vietnam but do not undergo standard export or import procedures at Vietnamese Customs.
(3) Goods purchased or sold at duty-free shops.
(4) Goods temporarily imported or temporarily exported within given periods of time, which are then re-exported or re-imported such as: goods for display at exhibitions, fairs and product showcases; documentation for conferences, seminars, scientific research, education, sports competitions, cultural performances, art performances, medical examination and treatment, product development and research; means of transport, containers and transport-related equipment.
(5) Goods crossing Vietnam’s territory simply for the purposes of transit and transshipment.
(6) Specific goods types:
- Goods under operational lease or charter contracts (aircraft, vessel, machinery, equipment) where no transfer of ownership of the goods takes place upon expiration of the lease;
- The Government of Vietnam’s goods delivered to or received from diplomatic representative missions, consular offices, or representative offices at international organizations of Vietnam abroad;
- Goods delivered from/to or received by/from diplomatic representative missions, consular offices of foreign countries, or representative offices of international organizations located in Vietnam;
- Monetary gold: Gold involved in transactions conducted by the State Bank of Vietnam or exported or imported by organizations authorized by the State Bank of Vietnam for purposes of monetary reserve and balance in accordance with law regulations;
- Coins in circulation, and issued banknotes, checks and securities in circulation;
- Goods used as empty means for goods carriage purposes: Containers, barrels, bottles, and similar items utilized on a rotational basis solely for goods carriage purposes;
- Products or contents transmitted electronically (software, audio/video products, films, e-books, and others);
- Media of storage of information and image, containing softwares produced upon request or under specific purchase orders; or original films, artworks, television programs, art performance, etc.);
- Goods illegally leaving or entering Vietnam’s territory;
- Goods brought into or taken out of Vietnam’s customs territory for repair or maintenance which does not change the origin of such goods;
- Exported or imported goods that constitute weapons or equipment intended to safeguard national interests, sovereignty, and security, falling under state secret lists;
- Waste or scrap that has no commercial value.”
c) Calculation method
“Time of import and export statistics: Time of statistics is the time customs offices accept registration of customs declaration forms.
Any changes in the customs declaration forms made during the customs procedures will be updated in the customs information system and reflected in statistical reports.
Within 90 days after the end of the reporting year, the statistical agencies cease updating any changes made to the customs declaration forms.
Statistical value of exports and imports:
- Statistical value of goods subject to export or import tax and other related taxes during the implementation of export or import procedures is the dutiable value of the goods.
- Statistical value of goods not subject to export or import tax and other related taxes during the implementation of export or import procedures is the declared value as accepted by the customs agencies.
- Statistical value of exports and imports calculated in US Dollar (USD). Customs agencies shall, based on applicable regulations on the exchange rate for taxing exports and imports, convert foreign currencies to US Dollar.
Determination of the statistical value in specific cases:
- For once-registered customs declaration forms for multiple import or export, the statistical value is the actual value of goods upon importation or exportation.
- Banknotes, coins and valuable papers not for circulation or not in circulation: Statistical value means the the cost of producing those banknotes, coins, or valuable papers (not their face value);
- Intermediate storage media for containing the information, including magnetic tapes and discs, CD-ROMs, smart cards and other intermediate storage media, whether recorded with data or not, excluding those produced upon request or under specific purchase orders: The full customs value of these goods must be recorded (not just the value of the intermediate storage media without data recorded);
- For goods allowed for filling temporarily calculated prices in customs declaration forms, their statistical value must be adjusted when their official prices are available on the amended or supplemented declaration forms;
- Goods for processing, manufacturing, assembly: The total value of raw materials prior to processing, manufacturing, or assembly and the total value of the finished products returned after processing, manufacturing, or assembly are recorded;
- For transactions for which value declaration is not required (for example, goods barter, humanitarian aid goods, etc.), the value of goods in statistics will be determined according to the principle of customs valuation;
- Returned goods: Their statistical value is the value of the goods at the value of the initial export or import transaction;
- Exported or imported electricity: The statistical value is the value declared on the customs declaration forms;
- For goods under financial lease contracts: their statistical value is calculated based on selling prices of similar goods, excluding accompanying services provided under the contracts, such as training and maintenance expenses and financial charges.
Currencies and exchange rates: The statistical value of exports and imports is calculated in US Dollar (USD). Customs agencies shall, based on applicable regulations on the exchange rate for taxing exports and imports, convert foreign currencies used in the the statistics.
Units of calculation in statistics means the converted units of measurement used in statistical forms. Other units of calculation of quantities for statistical purposes shall be converted into a unified unit of calculation, based on data from the customs dossiers.
Countries being trading partners:
For exportation: The statistics shall be according to “country or territory of final destination of goods”, meaning the country or territory to which, at the time of exportation, the customs declarant knows Vietnam's goods will be shipped for unloading, not counting those where goods are transshipped or in transit.
For importation: The statistics shall be according to “country or territory of origin”, meaning the country or territory where the goods were grown, extracted, produced, or processed, under Vietnam’s regulations on goods origin.”
2. Main disaggregation
- The Vietnamese import, export nomenclature;
- Country or territory of final destination of goods (for exportation), referring the country or territory to which, at the time of exportation, the customs declarant knows Vietnam's goods will be shipped for unloading, not counting those where goods are transshipped or in transit.
- Country or territory of origin (for importation), referring the country or territory where the goods were grown, extracted, produced, or processed, under Vietnam’s regulations on goods origin.
- The methods of transportation for exports/imports are categorized by: air transport, waterway transport, road transport, and other types.
- Province, centrally-run city: The data for each province or centrally-run city is compiled from the export/import customs declaration forms of all businesses, agencies, organizations, and individuals whose identification numbers are registered in such province or centrally-run city.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: National statistical reporting regime.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Finance;
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office).
17.17.1. Total number of public-private partnership investment projects
1. Definition and calculation method
Public-private partnership investment project (hereinafter referred to as PPP project) means a set of proposals related to investment in providing public products and services by carrying out one or more than one of the following activities:
+ Building, operating and commercially operating infrastructure facilities or systems;
+ Renovating, upgrading, expanding, modernizing, operating and commercially operating existing infrastructure facilities or systems;
+ Operating and commercially operating existing infrastructure facilities or systems.
- Investment in the form of public-private partnership means a form of investment effected on the basis of definite-term cooperation between the State and private investors through signing and performing PPP project contracts in order to attract private investors to participate in PPP projects.
2. Main disaggregation
- Field of investment;
- The total investment amount;
- State capital amount in a PPP project;
- Type of contract;
- Contract performance duration.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
4. Data sources: Annual PPP implementation report.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis: The Ministry of Planning and Investment.
17.19.1. Proportion of birth registrations
1. Definition and calculation method
Proportion of birth registrations means the percentage of persons whose births were registered compared to the total population in the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of birth registrations (%) |
= |
Number of persons whose births were registered |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
For the disaggregation of ethnicity, the publication frequency is every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Inter-censal population and housing survey;
- Population change and family planning survey;
- National population database;
- Electronic civil status database;
- Specialized population data warehouse.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Public Security; the Ministry of Health; the Ministry of Justice.
17.19.2. Proportion of death registrations
1. Definition and calculation method
The number of deaths registered is the number of deaths that have been registered for death registration during the study period. The number of deaths registered includes cases of persons declared dead by court judgment/decision and recorded in the civil status change register in accordance with the Law on Civil Status, cases of timely and overdue death registrations.
Proportion of birth registrations means the percentage of persons whose deaths were registered compared to the total population in the reporting period.
Calculation formula:
|
Proportion of death registrations (%) |
= |
Number of persons whose deaths were registered |
x |
100 |
|
The total population |
2. Main disaggregation
- Gender;
- Ethnicity;
- Province, centrally-run city;
- Socio-economic region.
3. Publication frequency: Annually.
For the disaggregation of ethnicity, the publication frequency is every 5 years.
4. Data sources
- Population and housing census;
- Inter-censal population and housing survey;
- Population change and family planning survey;
- National population database;
- Electronic civil status database;
- Specialized population data warehouse.
5. Agency in charge of collection and synthesis
- Agency assuming the prime responsibility: The Ministry of Planning and Investment (the General Statistics Office);
- Coordinating agency: The Ministry of Public Security; the Ministry of Health; the Ministry of Justice.
VIETNAMESE DOCUMENTS
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT PDF (Original)
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT PDF (Original)
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
ENGLISH DOCUMENTS
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT DOC (Word)
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here
 Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT PDF
Circular 02/2025/TT-BKHĐT PDF
This utility is available to subscribers only. Please log in to a subscriber account to download. Don’t have an account? Register here



